Table of Contents
Protecting Your macOS Device From Atomic macOS Stealer Malware- AMOS Malware
It is a known fact that Apple is growing its market in smartphones to mac books by releasing powerful exciting and more productive products over the years. This made threat actors create more malware programs to target Apple’s products. If you have been following cybersecurity blogs or intelligence for a year, MacStealer, RustBucket, and DazzleSpy are a few good examples, which show how threat actors are actively working on macOS exploits. There is a new addition to this list. Atomic macOS Stealer Malware (AMOS Malware).
Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) recently uncovered a Telegram channel promoting a new information-stealing malware, dubbed Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS). This malware is specifically engineered to target macOS users and pilfer sensitive information from their devices. The research team also reveals that the authors of this information stealer are kept on sale on a telegram channel for a hefty price of $1,000 per month. Let’s dive deep into this report published by Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs.
Capabilities of the Atomic macOS Stealer Malware
Before we start the technical details, let’s see what the information stealer can do. AMOS is engineered to extract a wide array of information from compromised devices.
Keychain passwords
Comprehensive system information
Files from the desktop and documents folder
macOS password
(Source: cyble.com) Keychain password extraction
According to Cyble researchers, the Atomic macOS Stealer malware is also capable of extracting information such as auto-fill data, passwords, cookies, wallets, and credit card information from multiple web browsers and various cryptocurrency wallets, including Atomic, Binance, Coinomi, Electrum, and Exodus. Moreover, the developers provide threat actors with a ready-to-use web panel for efficiently managing their victims.
Authors of the Atomic macOS Stealer malware are consistently refining the malware, introducing new capabilities to enhance its effectiveness. The most recent update to the malware was publicized on April 25th via a Telegram post, showcasing its latest features. This move has made the malware an even more dangerous threat not only for macOS users but for crypto-wallet users too.
What Atomic macOS Stealer Malware Promised to Sell to Their Clients (Threat Actors)?
Authors of the Atomic macOS Stealer malware offer these services to their clients for the cost of $1000 per month.
A web panel for managing victims
MetaMask brute-forcing for stealing seed and private keys
Crypto checker
DMG installer
After successfully infiltrating a victim’s device, the TA shares the stolen data logs via Telegram.
Deceptive Delivery and Infiltration Techniques
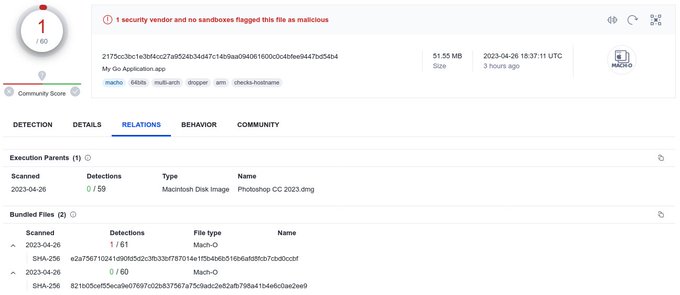
As per the technical details shared by CRIL, The Atomic macOS Stealer disguises itself as an unsigned disk image file (Setup.dmg). Once executed, the malware prompts the victim to enter their system password on a fake prompt. This tactic, also employed by MacStealer, allows the malware to escalate privileges and perform its malicious activities.
If you want to know about the infiltration technique, researchers say that the infiltration technique still remains unclear. However, it is likely that users are tricked into downloading and executing the malicious software, believing it to be legitimate. For instance, the Atomic stealer artifact discovered on VirusTotal on April 24, 2023, was named “Notion-7.0.6.dmg,” masquerading as the popular note-taking app. Other samples found by the MalwareHunterTeam were distributed as “Photoshop CC 2023.dmg” and “Tor Browser.dmg.” All that matters is the delivery of the malware, it doesn’t matter either by exploiting system vulnerabilities or served by phishing websites or emails.
Data Exfiltration and Transmission Process
(Source: cyble.com) Exfiltrated data
Upon successful infiltration, Atomic macOS Stealer proceeds to gather system metadata, files, iCloud Keychain, and information stored in web browsers (e.g., passwords, autofill, cookies, credit card data) and crypto wallet extensions. The collected data is compressed into a ZIP archive and transmitted to a remote server hxxp[:]//amos-malware[.]ru/sendlog by encoding the ZIP file in Base64 format. The ZIP file containing the compiled information is then forwarded to pre-configured Telegram channels. Please read the complete technical analysis here.
(Source: cyble.com) Collected system information
How to Protect Your macOS Device From Atomic macOS Stealer Malware?
To fortify your defenses against cyber threats like the Atomic macOS Stealer malware, it is crucial to follow a set of cybersecurity best practices. These proactive measures create a robust first line of defense against attackers and help ensure the safety of your data and devices. Below is a list of recommended best practices for macOS users:
Download software from trusted sources: Always download and install software from the official Apple App Store to minimize the risk of installing malicious applications.
Invest in reputable security software: Use a reliable antivirus and internet security software package to protect your system from malware and other threats.
Create strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication: Use unique, complex passwords for all your accounts and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible to add an extra layer of security.
Utilize biometric security features: Enable biometric security features, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, to unlock your device and add another layer of protection.
Exercise caution with email links: Be cautious when opening links received via email, especially if they are from unknown senders, as these could be phishing attempts or lead to malicious websites.
Manage permissions carefully: Be mindful when granting permissions to apps and websites, ensuring that you only give access to essential features and services.
Keep your devices and software updated: Regularly update your devices, operating systems, and applications to patch vulnerabilities and improve overall security.
By adhering to these cybersecurity best practices, macOS users can significantly enhance their protection against cyber threats and minimize the risk of falling victim to attackers.
Corporate companies should collect all the IOCs and block them on their all perimeter security devices. If possible, conduct an audit or scan for the persistence of the malware file or network communication.
MITRE ATT&CK® Techniques
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Execution | T1204.002 | User Execution: Malicious File |
| Credential Access | T1110 | Brute Force |
| Credential Access | T1555.001 | Keychain |
| Credential Access | T1555.003 | Credentials from Web Browsers |
| Discovery | T1083 | File and Directory Discovery |
| Command and Control | T1132.001 | Data Encoding: Standard Encoding |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C&C Channel |
Indicator of Compromise:
Crypto Wallet Extension
The table below lists the crypto wallets with respective browser extension IDs targeted by the malware.
| acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch | Rabby Wallet |
| aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg | Coin98 Wallet |
| afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc | Math Wallet |
| aholpfdialjgjfhomihkjbmgjidlcdno | Exodus Web3 Wallet |
| aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp | Station Wallet |
| amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih | Wombat – Gaming Wallet for Ethereum & EOS |
| apnehcjmnengpnmccpaibjmhhoadaico | CWallet |
| bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp | Hycon Lite Client |
| bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa | Phantom |
| bocpokimicclpaiekenaeelehdjllofo | XDCPay |
| cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk | EVER Wallet |
| cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje | LeafWallet |
| cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne | Jaxx Liberty |
| cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj | Finnie |
| cmndjbecilbocjfkibfbifhngkdmjgog | Swash |
| cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae | Auro |
| copjnifcecdedocejpaapepagaodgpbh | Freaks Axie |
| cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao | NeoLine |
| dhgnlgphgchebgoemcjekedjjbifijid | Crypto Airdrops & Bounties |
| dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm | Cyano |
| dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap | Keplr |
| efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk | Martian Wallet for Sui & Aptos |
| egjidjbpglichdcondbcbdnbeeppgdph | Trust Wallet |
| ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb | Yoroi |
| fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp | BinanceChain |
| fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh | Oxygen |
| flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel | ICONex |
| fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec | Ronin |
| fnnegphlobjdpkhecapkijjdkgcjhkib | Harmony Wallet |
| hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn | KHC |
| hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf | XDEFI |
| hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad | Coinbase |
| hnhobjmcibchnmglfbldbfabcgaknlkj | Flint Wallet |
| hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln | Guarda |
| ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec | TronLink |
| imloifkgjagghnncjkhggdhalmcnfklk | Trezor Password Manager |
| jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf | Polymesh |
| klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd | ZilPay |
| kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj | iWallet |
| kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn | Liquality |
| lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik | DAppPlay |
| mfhbebgoclkghebffdldpobeajmbecfk | Starcoin |
| mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh | TezBox |
| nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk | CLW |
| nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn | Metamask |
| nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad | Nabox |
| nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm | MewCx |
| nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd | Byone |
| nphplpgoakhhjchkkhmiggakijnkhfnd | Ton |
| ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc | Temple |
| pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk | KardiaChain |
| pnndplcbkakcplkjnolgbkdgjikjednm | Tron Wallet & Explorer – Tronium |
| pocmplpaccanhmnllbbkpgfliimjljgo | Slope |
| ppdadbejkmjnefldpcdjhnkpbjkikoip | Oasis |
Command and Control (C&C)
hxxp[:]//amos-malware[.]ru/sendlog
amos-malware[.]ru
Setup.dmg
5e0226adbe5d85852a6d0b1ce90b2308
0a87b12b2d12526c8ba287f0fb0b2f7b7e23ab4a
15f39e53a2b4fa01f2c39ad29c7fe4c2fef6f24eff6fa46b8e77add58e7ac709
We hope this post would help you know know how to protect your macOS device from Atomic macOS Stealer Malware (AMOS Malware). Please share this post and help to secure the digital world. Visit our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium & Instagram, and subscribe to receive updates like this.
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.