Table of Contents
Criminals Target Google Ads Accounts Through Sophisticated Phishing Scam
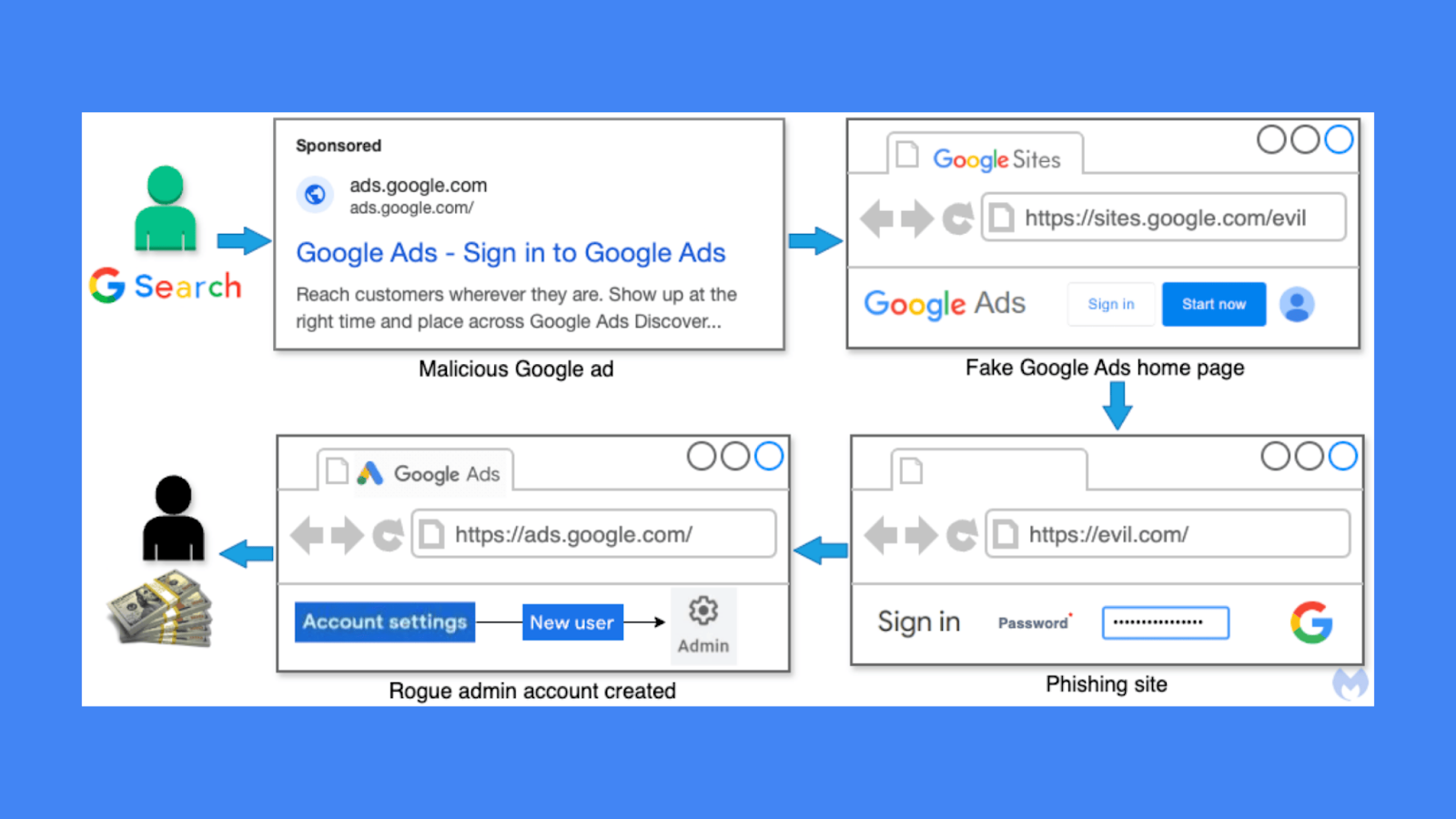
In a brazen digital assault, cybercriminals are launching a sophisticated phishing campaign specifically targeting Google Ads account holders, exploiting the very platform they aim to compromise. Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a multi-pronged attack strategy that leverages fraudulent advertisements and impersonation techniques to steal user credentials and hijack advertising accounts.
A malicious ad masquerading as Google Ads
The attack begins with meticulously crafted sponsored advertisements that appear authentic, designed to lure advertisers into clicking what seems to be legitimate Google Ads login pages. These deceptive ads are strategically placed within Google Search results, making them virtually indistinguishable from genuine Google advertisements.
Process flow for this Google Ads heist campaign
Threat actors are employing an ingenious technique by utilizing Google Sites as an intermediate landing page, which allows them to bypass standard security protocols. By hosting phishing pages on sites.google.com, they create a veneer of legitimacy that makes detection extremely challenging. The fake sites closely mimic the original Google Ads interface, tricking unsuspecting users into entering their login credentials.
A malicious Google Sites page impersonating Google Ads
Once users input their account information, the phishing kit springs into action, collecting unique identifiers, cookies, and login credentials. The stolen information is then transmitted to remote servers controlled by the cybercriminals. In many instances, victims receive notifications about suspicious login attempts, often originating from locations like Brazil, but these warnings frequently arrive too late to prevent account compromise.
Researchers have identified multiple threat actor groups behind these campaigns, with the most prolific being Portuguese-speaking operators likely based in Brazil. Another group appears to be operating from Asia, specifically targeting advertising accounts from regions like Hong Kong and China. A third group, potentially from Eastern Europe, is also utilizing similar tactics.
The ultimate goal of these attacks extends beyond simple credential theft. Cybercriminals aim to leverage the hijacked Google Ads accounts to perpetuate further malicious activities, including distributing additional phishing links, spreading malware, and generating revenue through fraudulent ad campaigns.
Google has acknowledged the ongoing threat, stating that they expressly prohibit ads designed to deceive users and steal their information. The company reports taking significant enforcement actions in 2023, including removing over 3.4 billion ads and suspending more than 5.6 million advertiser accounts.
Cybersecurity experts recommend that advertisers remain vigilant, enable two-factor authentication, regularly monitor account activity, and be wary of suspicious login attempts or unexpected advertisements. Users should also be cautious of sponsored results and verify the authenticity of login pages before entering credentials.
The sophistication of these attacks underscores the evolving landscape of cybercrime, where threat actors continuously develop more complex methods to exploit digital platforms and user trust. As advertising platforms become increasingly lucrative targets, organizations and individual users must remain proactive in their cybersecurity practices.
Researchers continue to track and report these malicious campaigns, working closely with platforms like Google to mitigate risks and protect users from potential financial and reputational damage caused by such sophisticated phishing schemes.
Found this article interesting? Keep visit thesecmaster.com, and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium, and Instagram and subscribe to receive tips like this.
You may also like these articles: Here are the 5 most contextually relevant blog posts:
Anthony Denis
Anthony Denis a Security News Reporter with a Bachelor's in Business Computer Application. Drawing from a decade of digital media marketing experience and two years of freelance writing, he brings technical expertise to cybersecurity journalism. His background in IT, content creation, and social media management enables him to deliver complex security topics with clarity and insight.