Table of Contents
Hackers Steal 390000 WordPress Credentials Through Malicious GitHub Repos
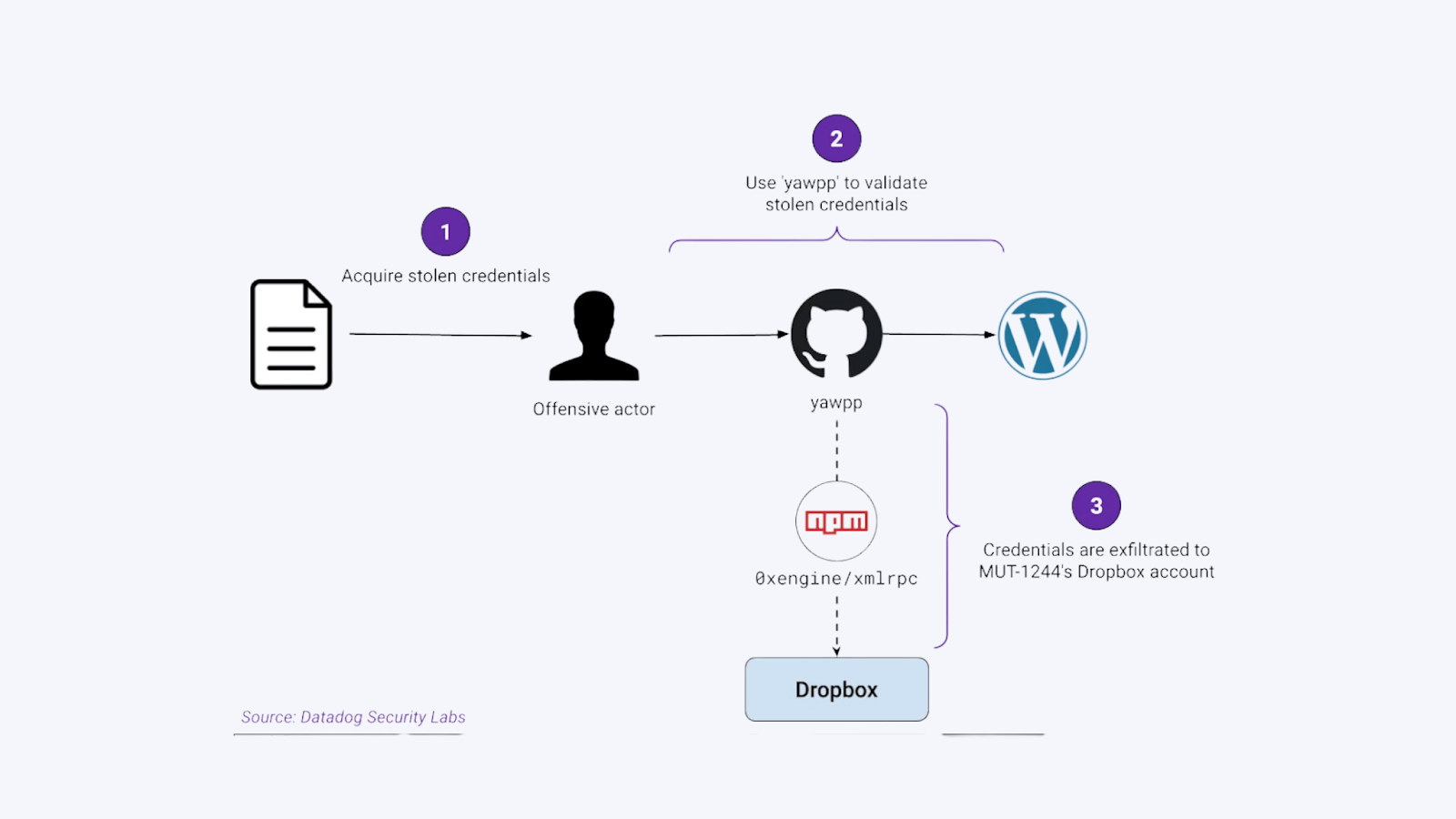
A threat actor tracked as MUT-1244 has successfully stolen over 390,000 WordPress credentials in a large-scale campaign targeting other threat actors using a trojanized WordPress credentials checker hosted on GitHub.
Researchers at Datadog Security Labs discovered that the campaign not only involved stealing credentials but also compromised systems of hundreds of victims, including red teamers, penetration testers, security researchers, and malicious actors. Along with WordPress credentials, the attackers also exfiltrated sensitive information such as SSH private keys and AWS access keys.
The campaign utilized two primary attack vectors: trojanized GitHub repositories hosting fake proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits and a targeted phishing campaign. These methods were designed to deliver a sophisticated second-stage payload capable of dropping cryptocurrency miners and stealing system information.
The malicious repository "github[.]com/hpc20235/yawpp," which claimed to be a WordPress posting tool, contained scripts for validating WordPress credentials. However, it also harbored a rogue npm dependency named @0xengine/xmlrpc that deployed malware. The package was previously active on npm and attracted approximately 1,790 downloads before being removed.
Researchers noted that the threat actor, dubbed MUT-1244, leveraged multiple techniques to spread malware, including:
Embedding backdoors in configure compilation files
Hiding malicious payloads inside PDF files
Using Python droppers
Incorporating malicious npm packages in project dependencies
The phishing component involved sending emails to academics, tricking them into executing commands under the guise of a kernel upgrade. This approach marks the first documented "ClickFix-style" attack targeting Linux systems.
The attackers strategically exploited trust within the cybersecurity community, successfully compromising dozens of machines by disguising malware as legitimate tools and exploit code. The campaign's sophistication lies in its ability to blend malicious activities with seemingly genuine development resources.
Datadog Security Labs estimates that hundreds of systems remain compromised, with ongoing infections continuing as part of this extensive campaign. The researchers emphasized the importance of vigilance and thorough vetting of tools and sources before use.
The investigation reveals a broader trend of threat actors increasingly targeting security professionals by leveraging seemingly legitimate development resources and exploiting the community's curiosity about vulnerability research and proof-of-concept exploits.
The findings underscore the critical need for heightened security awareness and rigorous validation of tools, especially those circulating within technical communities focused on security research and vulnerability testing.
Found this article interesting? Keep visit thesecmaster.com, and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium, and Instagram and subscribe to receive tips like this.
You may also like these articles: Here are the 5 most contextually relevant blog posts:
How Attackers Abused Google Search to Distribute Trojanized AnyDesk Installer
PyPI Under Fire as Malicious Package 'Fabrice' Discovered Stealing AWS Keys
LottieFiles' 'lottie-player' NPM Package Compromised in Supply Chain Attack
JarkaStealer Malware Discovered in Fake AI Integration Packages on PyPI Repository
A New Javascript Injection Campaign on WordPress Websites Try Pushing RATs
Anthony Denis
Anthony Denis a Security News Reporter with a Bachelor's in Business Computer Application. Drawing from a decade of digital media marketing experience and two years of freelance writing, he brings technical expertise to cybersecurity journalism. His background in IT, content creation, and social media management enables him to deliver complex security topics with clarity and insight.