Table of Contents
Microsoft Signed UEFI Bootloader Vulnerability Enables Malicious Bootkit Execution
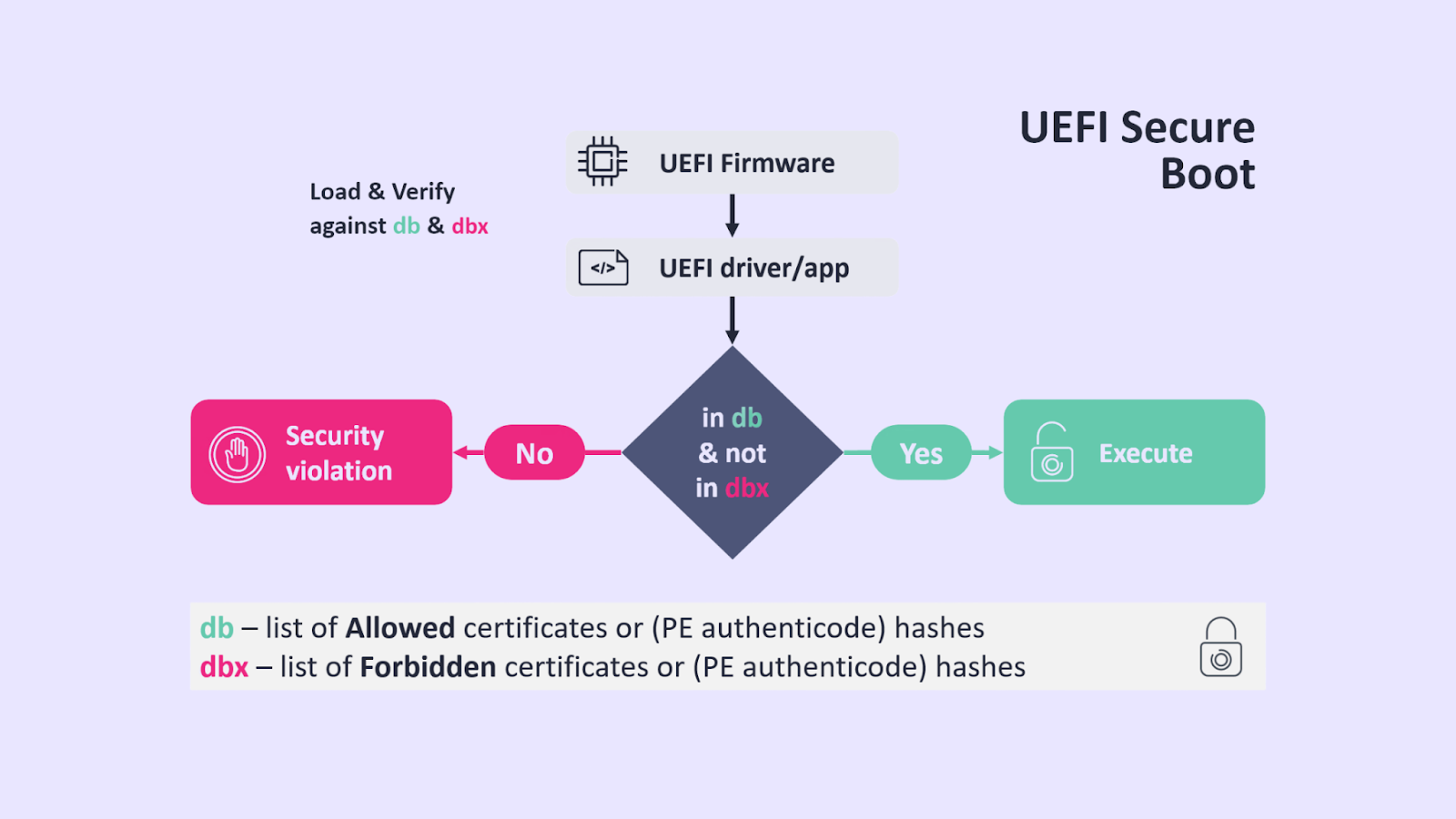
A critical security vulnerability has been discovered in a Microsoft-signed UEFI bootloader that could potentially allow attackers to bypass Secure Boot protections and execute malicious unsigned code during system startup.
Researchers from ESET have uncovered a significant security flaw affecting multiple real-time system recovery software suites across several technology companies. The vulnerability, assigned CVE-2024-7344, resides in a UEFI application signed by Microsoft's "Microsoft Corporation UEFI CA 2011" third-party UEFI certificate.
The vulnerability stems from the use of a custom PE loader that deviates from standard secure UEFI functions. This allows the loading of any UEFI binary - even an unsigned one - from a specially crafted file named cloak.dat during system startup, regardless of the UEFI Secure Boot state.
Affected software products include recovery solutions from various vendors such as Howyar Technologies, Greenware Technologies, Radix Technologies, SANFONG Inc., Wasay Software Technology, Computer Education System, and Signal Computer GmbH. The vulnerable versions span multiple software packages, with each vendor having specific version ranges impacted.
An attacker exploiting this vulnerability could potentially execute unsigned code during the boot process in the UEFI context, even before the operating system loads. This grants them a powerful mechanism to install persistent malware that can survive system reboots and potentially evade traditional security detection mechanisms.
To successfully exploit the vulnerability, an attacker would need elevated privileges to deploy malicious files to the EFI system partition. This typically requires local administrator access on Windows or root access on Linux systems.
The research team responsibly disclosed their findings to the CERT Coordination Center in June 2024. Subsequently, the affected vendors addressed the issue in their products, and Microsoft revoked the vulnerable binaries during its January 14, 2025 Patch Tuesday update.
Mitigation strategies include applying the latest UEFI revocations, managing access to EFI system partition files, customizing Secure Boot configurations, and implementing remote attestation with Trusted Platform Module (TPM) technologies.
The discovery raises broader questions about the security review processes for third-party UEFI applications and highlights the ongoing challenges in maintaining the integrity of firmware-level security mechanisms. Researchers emphasized that this is not an isolated incident, pointing to potential systemic issues in UEFI software development and certification processes.
For users and organizations, the primary recommendation is to ensure systems are updated with the latest security patches and to follow vendor guidelines for mitigating this specific vulnerability.
Found this article interesting? Keep visit thesecmaster.com, and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium, and Instagram and subscribe to receive tips like this.
You may also like these articles: Here are the 5 most contextually relevant blog posts:
Anthony Denis
Anthony Denis a Security News Reporter with a Bachelor's in Business Computer Application. Drawing from a decade of digital media marketing experience and two years of freelance writing, he brings technical expertise to cybersecurity journalism. His background in IT, content creation, and social media management enables him to deliver complex security topics with clarity and insight.