Table of Contents
New ZIP File Concatenation Technique Exploited by Hackers to Evade Windows Security
In a concerning development for cybersecurity professionals and Windows users alike, hackers have begun leveraging a sophisticated evasion technique known as ZIP file concatenation to deliver malicious payloads while evading detection by security solutions. This new trend, recently uncovered by cybersecurity researchers, exploits the differences in how various ZIP parsers and archive managers handle concatenated ZIP files.
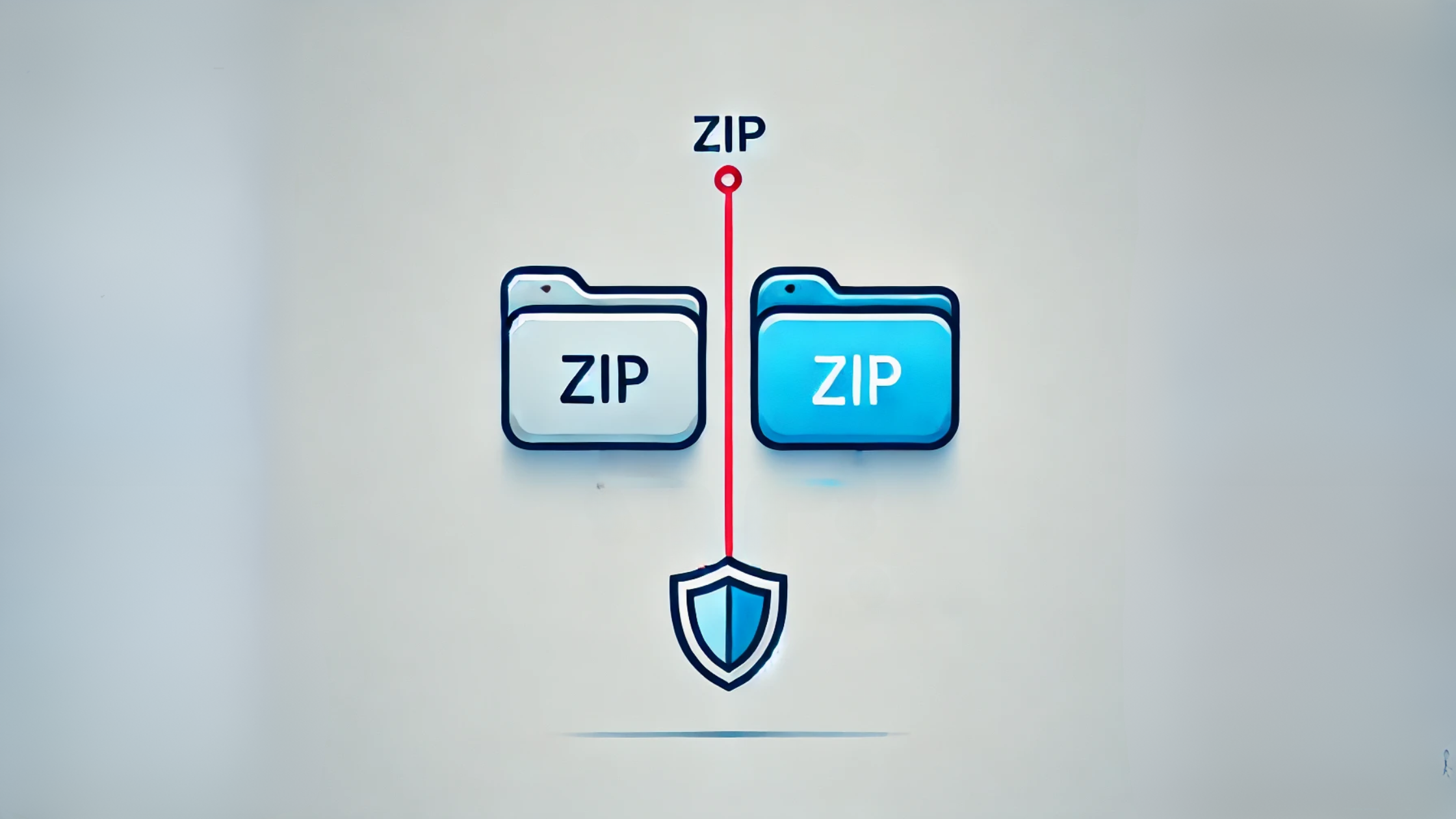
The attack method involves creating multiple separate ZIP archives, with malicious content hidden in one of them. These archives are then concatenated into a single file by appending the binary data of one file to another. The resulting file appears as one archive but contains multiple ZIP structures, each with its own central directory and end markers.
Perception Point, a cybersecurity provider, discovered this technique while analyzing a phishing attack that used a fake shipping notice to lure users. The attached file, disguised as a RAR archive, contained a trojan that leveraged the AutoIt scripting language to automate malicious tasks.
The effectiveness of this evasion tactic lies in how different ZIP parsing tools handle the concatenated files:
7zip only reads the first ZIP archive, which could be benign, potentially missing the malicious content.
WinRAR reads and displays both ZIP structures, revealing all files, including the hidden malicious payload.
Windows File Explorer may fail to open the concatenated file entirely or, if renamed with a .RAR extension, might only display the second ZIP archive.
This discrepancy in handling concatenated ZIPs allows attackers to bypass detection tools by hiding malicious payloads in parts of the archive that some ZIP readers cannot or do not access.
The implications of this technique are significant, as many security solutions rely on common ZIP handlers like 7zip or native OS utilities to scan archives for malicious content. This new method of concealment presents a challenge for cybersecurity professionals and highlights the need for more robust archive handling in security solutions.
To defend against this emerging threat, experts recommend:
Using security solutions that support recursive unpacking
Treating emails with ZIP or other archive file attachments with heightened suspicion
Implementing filters in critical environments to block related file extensions
In response to this threat, Perception Point has developed a proprietary anti-evasion algorithm called Recursive Unpacker. This algorithm is designed to detect and recursively unpack concatenated ZIP files, enhancing the detection of sophisticated malware that might otherwise go unnoticed.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it's crucial for both individuals and organizations to stay informed about these new techniques and ensure their security measures are up-to-date. The ZIP file concatenation exploit serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing cat-and-mouse game between cybercriminals and security professionals, emphasizing the need for constant vigilance and adaptation in the face of emerging threats.
Visit our website to get cybersecurity updates like this, thesecmaster.com, and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium, and Instagram and subscribe to receive tips like this.
You may also like these articles:
Anthony Denis
Anthony Denis a Security News Reporter with a Bachelor's in Business Computer Application. Drawing from a decade of digital media marketing experience and two years of freelance writing, he brings technical expertise to cybersecurity journalism. His background in IT, content creation, and social media management enables him to deliver complex security topics with clarity and insight.