Table of Contents
7 Foundational Principles of Privacy by Design
In today's hyper-connected world, where data is the new currency, the importance of data privacy cannot be overstated. From social media platforms tracking our every move to sophisticated AI algorithms analyzing our preferences, our personal information is constantly being collected, processed, and shared. But what if we could change the rules of the game? What if privacy wasn't an afterthought, but rather a fundamental building block of every system, product, and service we use?
That's the promise of Privacy by Design (PbD).
What is Privacy by Design?
Privacy by Design isn't just a set of guidelines or best practices; it's a paradigm shift in how we think about data privacy. It’s a commitment to proactively embedding privacy into the very fabric of our technological and business endeavors, long before any data is even collected. This holistic approach views privacy as an essential component, as critical as functionality, usability, or security.
PbD means integrating privacy seamlessly into the design of information technologies, networked infrastructure, and business practices. Think of it as baking privacy into the cake, rather than sprinkling it on top as an afterthought.
The core idea? Protecting customer data becomes a guiding force in the user experience.
Why is Privacy by Design Important?
Several compelling reasons underscore the growing importance of Privacy by Design in our digital age.
Public Opinion Demands It: A study by the Pew Research Center reveals that a significant majority of Americans are deeply concerned about data privacy:
* 85% believe the risks of data collection by companies outweigh the benefits.
* 76% feel there are little to no benefits from company data processing.
* 81% familiar with AI believe collected info will be used in uncomfortable ways.
* 80% believe it will be used in unintended ways.
Wavering Trust: These statistics highlight a growing erosion of trust between consumers and organizations that handle their data. PbD offers a way to rebuild that trust by demonstrating a genuine commitment to protecting user privacy.
The Rise of AI: The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence technologies further amplifies the need for PbD. As AI systems become more sophisticated and pervasive, it's crucial to ensure that privacy is built into their design from the outset. One of the ways of achieving is AI security.
Compliance and Legal Landscape: Privacy by Design is also increasingly important from a legal and regulatory standpoint. Many data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, explicitly promote the principles of PbD. Article 25 of the GDPR emphasizes "Data Protection by Design and by Default," requiring organizations to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from the very beginning.
It's a Strategic Asset: Implementing Privacy by Design isn't just about compliance; it's about creating a competitive advantage. By prioritizing privacy, organizations can build stronger relationships with their customers, enhance their brand reputation, and foster innovation. Automation elevates a privacy program to a strategic business asset. Privacy automation adapts to business needs, ensures agile compliance, and facilitates responsible use of technologies like AI. Consider leveraging automation to achieve this.
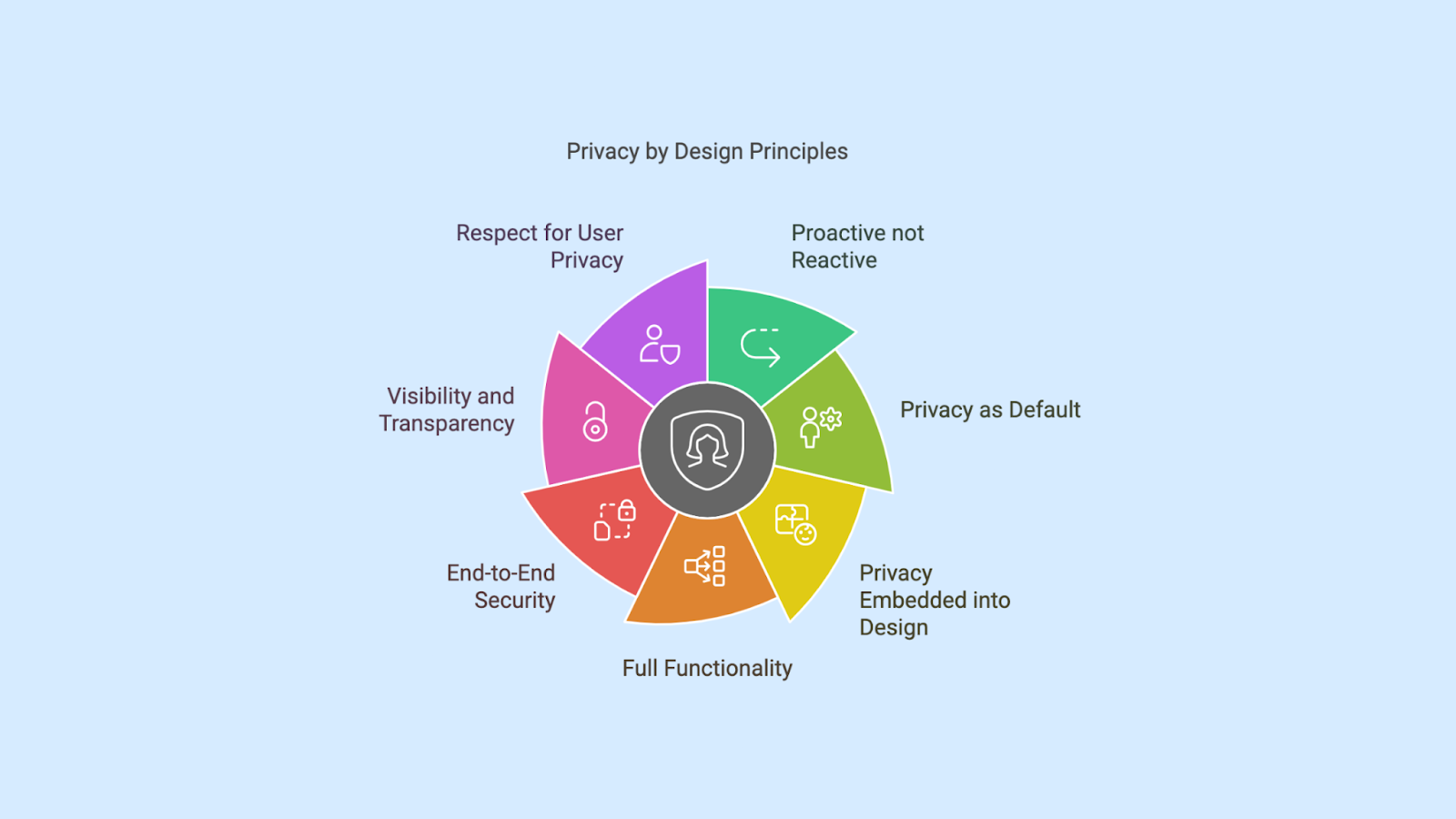
The 7 Foundational Principles of Privacy by Design
The cornerstone of Privacy by Design lies in its seven foundational principles, originally developed by Dr. Ann Cavoukian, the former Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario, Canada. These principles provide a comprehensive framework for embedding privacy into every stage of the design and development process.
Let's delve into each principle in detail:
1. Proactive not Reactive; Preventative not Remedial
This principle emphasizes the importance of anticipating and preventing privacy risks before they occur. Instead of reacting to breaches or violations after they've happened, PbD advocates for building processes and systems that actively prevent privacy intrusions from the outset. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments, identifying potential threats, and implementing proactive measures to mitigate those risks.
Actionable Advice: Focus on prevention and preparedness measures before a breach occurs. Implement robust detection and response processes, incident response, and business continuity plans. Identify potential threats and anticipate their occurrence.
2. Privacy as the Default Setting
This principle mandates that privacy should be the default setting in any system or service. This means that users shouldn't have to actively adjust settings or make choices to protect their privacy; privacy should be automatically set to the highest level of protection.
Key Default Settings:
Collection Limitation: Only collect data you're legally allowed to.
Data Minimization: Collect the minimum necessary data. Don't collect "just because."
Use, Retention & Disclosure Limitation: Only use data for agreed-upon purposes, don't retain it longer than needed, and only disclose if necessary.
Security: Implement technical and organizational measures to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data (e.g., encryption).
Actionable Advice: Scrub data sets to remove unnecessary data fields. Only retain personally identifiable information as long as needed.
3. Privacy Embedded into Design
Privacy should be an integral part of the design process, not an afterthought or a tacked-on feature. This means considering privacy implications at every stage of development, from the initial concept to the final implementation. Every decision should be filtered through a "privacy-first" mindset. Privacy impact assessments and security misconfiguration are key objectives to measure and mitigate potential breaches.
Actionable Advice: Make privacy impact assessments and risk assessments key objectives to measure and mitigate potential breaches.
4. Full Functionality – Positive-Sum, not Zero-Sum
This principle challenges the notion that privacy and functionality are mutually exclusive. PbD seeks to achieve a "positive-sum" outcome, where privacy is seamlessly integrated without compromising functionality or user experience. It's about finding creative solutions that optimize both privacy and usability.
Actionable Advice: Strive for a situation where security and privacy exist at total capacity together in tandem without causing difficulty to their operations. Don't assume trade-offs between privacy and user experience or security. Privacy can be a market mover.
5. End-to-End Security – Lifecycle Protection
This principle emphasizes the importance of securing data throughout its entire lifecycle, from collection to disposal. It involves implementing robust security measures at every stage, including encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention technologies. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility (CIA) throughout the data's lifecycle. Responsibility for security over personal information is key.
Actionable Advice: Implement security measures (CIA - confidentiality, integrity, availability) at every stage. Focus on responsibility for security over personal information. Data must be protected throughout its entire lifecycle (collection, storage, use, disposal). Security is fundamental to guaranteeing privacy.
6. Visibility and Transparency – Keep it Open
This principle promotes openness and transparency in data practices. Organizations should be transparent with users about how their data is collected, used, and shared. This involves providing clear and accessible privacy policies, obtaining informed consent, and offering users control over their data. Be open with users about privacy policies and procedures to build trust and accountability.
Actionable Advice: Create accessible and comprehensive policies and procedures. Ensure proper data protection when transferring data to third parties. Monitor, evaluate, and verify compliance. Document and communicate actions clearly and consistently. Have an accessible and effective complaint submission and resolution process. Consider independent verification of policies.
7. Respect for User Privacy – Keep it User-Centric
This principle places the individual at the center of data privacy considerations. Organizations should always consider the user's privacy interests and provide safeguards to protect their personal information. This includes empowering users to manage their own data, providing clear and user-friendly privacy controls, and actively seeking user engagement in the design process.
Actionable Advice: Require consent before data processing. Keep personal information accurate. Give individuals the right to access and correct their information. Focus on human-centered, user-centric, and user-friendly interfaces. Always consider user privacy interests and provide safeguards. The best user experience puts privacy first. Empower users to manage their own data. Actively seek user engagement in the process.
Implementing Privacy by Design: A Practical Guide
Implementing Privacy by Design requires a multi-faceted approach that involves cultural shifts, technical expertise, and ongoing commitment.
Here are some practical steps that organizations can take:
Conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs): Before launching any new product or service, conduct a PIA to identify potential privacy risks and develop mitigation strategies. Assess before you build.
Embrace Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is absolutely necessary for the intended purpose.
Utilize Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): Explore and implement PETs, such as encryption, anonymization, and pseudonymization, to protect data privacy.
Train Your Employees: Educate employees about data privacy principles and best practices.
Develop Clear and Accessible Privacy Policies: Communicate data practices in a transparent and user-friendly manner.
Establish a Privacy Governance Framework: Appoint a privacy officer and establish clear roles and responsibilities for data privacy. Champion in charge.
Continuously Monitor and Improve: Regularly review and update privacy practices to adapt to evolving threats and regulations. Incident response plan should be in place for the organization.
Conclusion: A Future Where Privacy Thrives
Privacy by Design is more than just a set of principles; it's a vision for a future where privacy is not an afterthought, but a fundamental human right. By embracing PbD, organizations can build trust with their customers, enhance their brand reputation, and foster innovation.
It's time to move beyond reactive compliance and embrace a proactive, preventative approach to data privacy. By embedding privacy into the very fabric of our technological and business endeavors, we can create a digital world where privacy thrives. The key is to keep the user's needs in focus.
Found this article interesting? Keep visit thesecmaster.com, and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium, and Instagram and subscribe to receive tips like this.
You may also like these articles:
India Passed Digital Personal Data Protection Bill (DPDPB)- What Does it Mean for a Common Man?
FTC Cracks Down on Major Data Brokers Banned from Selling Sensitive Location Data
List of Federal and State Data Privacy Laws in the United States
Managing Data Retention: Developing a Secure Information Lifecycle Strategy
What is Personal Information? And, How to Protect Personal Information?
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.