Table of Contents
The Power of Automation and Orchestration in Cybersecurity: A Closer Look at SOAR
SOAR made its first appearance on the scene of cyber security in the year 2015, when Gartner described it as an innovative, revolutionary technology within the field of cyber security. And now, in the year 2023, Security Orchestration Automation and Response has lived up to those expectations and is rapidly growing its presence rapidly, with the SOAR market estimated to grow to $550 million with 14.9% of CAGR.
The only thing which limits the market potential of this security program is that not all buyers seek to add automated responses to their security programs. However, many companies are still keen to learn about the role of automation and orchestration in cybersecurity and what benefits it can bring to their organization.
Read on to learn more about the peculiarities that are associated with SOAr and and find out the significance that it can play by the year 2023 and beyond.
What Is the Difference Between Automation and Orchestration?
Image Source: Bizagi
Automation is the process of automating one process or a smaller number of tasks (e.g., the deployment of an application). Orchestration involves managing multiple automated tasks in order to create a fluid workflow (e.g. installing an application, connecting it with the network, and connecting it with other applications).
In detail, automation allows you to create a single procedure that can run with no human involvement. Instead of having a staff member work on a task manually, computers can run a script and perform the task in a short time and as often as needed. Automation makes processes more reliable and efficient.
While orchestration is the act that manages a set of automated tasks that create an integrated workflow, a sysadmin configures an automated system that performs several tasks according to a detailed list of guidelines and rules. Orchestration could be coordinating, configuring, and administering multiple apps, computer systems, datasets, middleware, and technologies. Orchestration allows IT professionals to tackle complicated work and processes.
| Features | Automation | Orchestration |
| Tools and functionalities | Interconnected tools and functionalities are utilized | It counts on various resources and ensures an interoperability level between the resources |
| Intervention from personnel | Requires to complete a number of manual tasks to ensure the deliverance of a completely new environment | Needs less personnel intervention to complete tasks |
| Use of Resources | Minimal usage of resources | Cloud resources are utilized efficiently |
| Third-party reporting services | It can need a third-party reporting service to send data | Monitors and alerts system on it’s own for the processes |
The Importance of Automation and Orchestration in Cybersecurity
Security orchestration and automation can be utilized to delegate low-priority and repetitive tasks, allowing organizations to concentrate on work and further enhancing the response to incidents. Below is an in-depth explanation of the reason orchestration and automation are important for cybersecurity:
Security Alertness
Because cybercriminals are smart, security officers of a firm shouldn’t ignore security-related training. Cybersecurity personnel should keep an eye on the impact of their security education and develop new and unique methods to pass on important information to their coworkers or outsource their security training.
Evaluations of Security Progress
Evaluations are crucial to an in-depth understanding of the cybersecurity awareness of an organization.
In particular, vulnerability assessments are the automatic solution for the same thing. They are based on the information on security flaws that have been previously identified. But, it can’t assess security system flexibility in the form of classy attacks or strange antagonistic behavior.
A more thorough assessment method is required to prove that the business can protect itself. For instance, solutions like red teaming and penetration testing, which are mostly manual and rely on the expertise and knowledge of a specialist, could replicate an attack on the internet.
This is a combination of techniques and processes adapted to the particular needs of an organization’s security capabilities, thereby promoting genuine attacks.
Sensing Advanced Threats
Even the best-tuned sensors can’t detect prior, unnoticed negative actions. The most common attacks are a sequence of effective and autonomous actions that could be easily connected to the system administrator or a series of user-defined actions. But this does not mean artificial Intelligence can’t spot risks.
In reality, it can efficiently handle any attack. If it is properly fixed, it can reduce the number of professional jobs. A great understanding of analytic techniques, unique capabilities, and the continuous change of algorithm success is required to implement an effective joint force strategy that involves human involvement paired with AI.
Alert for Fatigue
The increasing amount of alerts generated by the numerous tools used by SOCs can cause alert fatigue that can affect an organization’s security. It is possible to ignore real threats and spend too much time analyzing false positives.
Growth in the Number of Tools and Solutions
Each security team employs many different instruments and strategies. In addition to the issue of alert fatigue that results from false alarms, this plethora of tools makes analysts spend a lot of time hopping from screen to screen and making connections manually, reducing efficiency.
Talent Shortage
If you’re looking to hire the perfect person for your security staff, you search for them, educating them and hoping to utilize their abilities to their full potential. Do you prefer them to refrain from using their valuable time and knowledge to do repetitive, boring tasks?
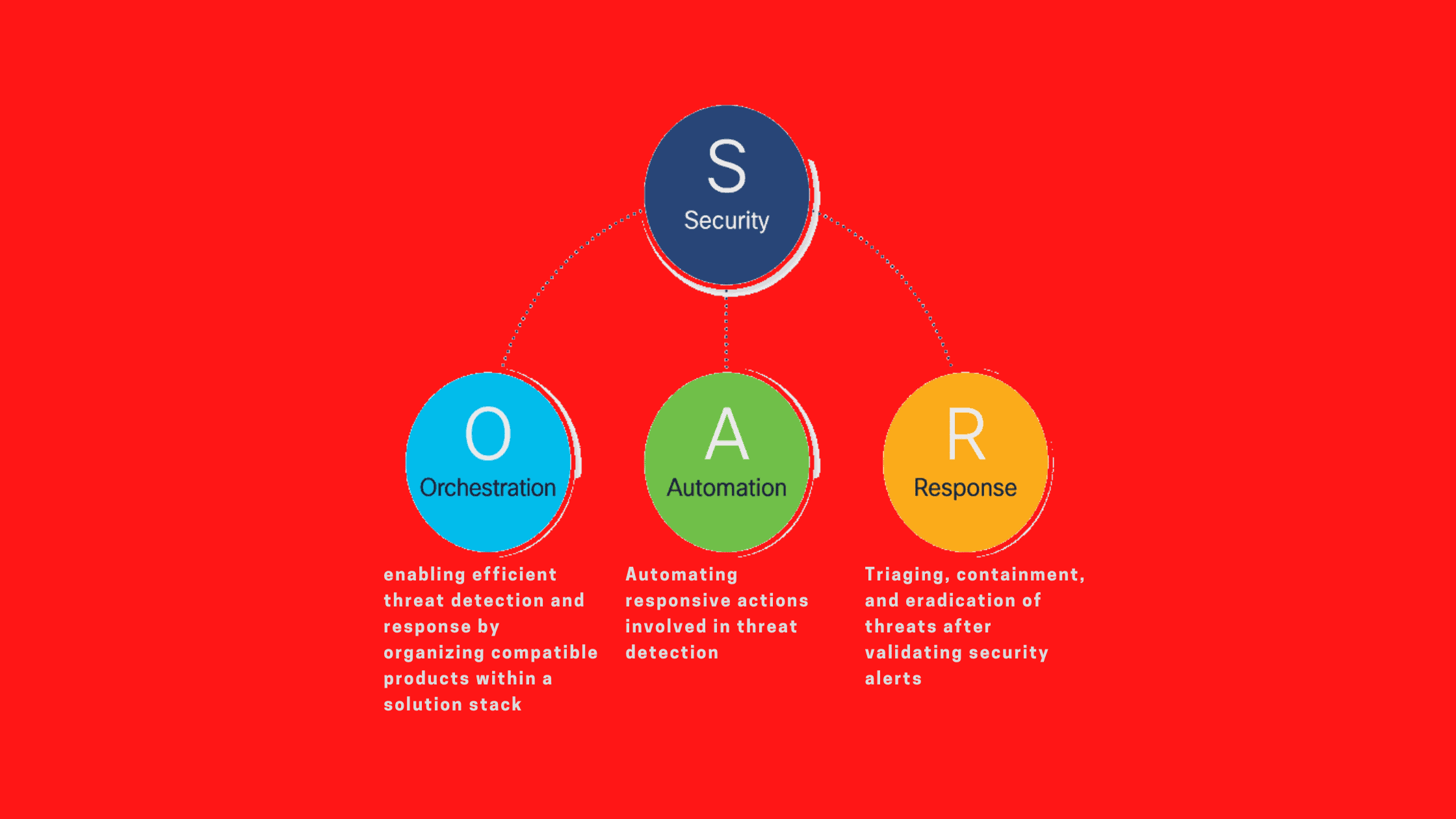
What is Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR)?
Image Source: Cisco Blogs
“Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR) refers to a range of tools and software that help organizations improve security operations in three main areas: vulnerability and threat management, emergency response security automation.”
SOAR is a term used to describe technologies that allow organizations to collect and monitor inputs by security operation teams. The tools enable organizations to design processes for responding to incidents in a digital workflow format.
Security Orchestration
Security orchestration (SO) is the computer-based orchestration of a set of security actions that are interdependent across an intricate infrastructure. It makes sure that all of the security instruments you use — even other tools that are not security-related are in sync, automating the tasks of different tools and workflows.
SO assists in investigating incidents, the response phase, and eventually, resolution. It also eliminates the need for security experts to use various screens and systems, putting all the information in one place and showing it all on a single dashboard.
Security Operation
Security operations sometimes referred to as SecOps, refers to an organization that combines internal security of information and IT operations procedures to improve collaboration and minimize risk.
Security operations can break cultural and organizational barriers and reduce conflicts and inefficiencies by establishing a security-first mentality and integrating security into IT operations procedures. With SecOps, threat, and risk mitigation becomes an integral part of the job, and personnel working in operations collaborate with security experts to minimize security risks without impacting business agility.
Incident Response
Incident response refers to the method that an organization uses to deal with the aftermath of a cyberattack or data breach, as well as the method by which the company attempts to deal with the effects of the cyberattack or the breach (the “incident”).
In most cases, incident response is carried out by an organization’s computer incident resolution team (CIRT), which is also known as a cyber-incident response team. They are accountable for responding to cyber-attacks, viruses, and other incidents that could be catastrophic for companies that are facing major security threats. Apart from technical experts dealing with specific dangers, they should also comprise experts who can advise business executives on how to communicate following such events.
What is Security Incident & Event Management (SIEM)?
Image Source: wallarm
Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) is the method of tracking, identifying, and analyzing security incidents or incidents in a live IT environment. It gives a complete and central view of the security situation that is part of the IT infrastructure.
SIEM is implemented through devices, software, appliances, or a combination. The primary characteristics of SIEM are as follows:
Retention: Storing data over prolonged periods makes it possible to make decisions from more comprehensive data sets.
Dashboards: Used to analyze (and visualize) data to identify patterns, activities, or data that do not conform to a standard pattern.
Correlation: A method of separating data into useful pieces that are similar and have the same characteristics. The objective is to convert knowledge into actionable information.
Alerting: If data is collected or identified to generate certain responses, like alerts or possible security issues, SIEM tools can activate specific protocols to notify users of alerts, for example, notifications directly to dashboards or an automated text message or email.
Information Aggregation (DA): The information may be gathered from a variety of websites once SIEM is installed, including servers as well as networks, databases software, and email systems. The aggregator is also an aggregator prior to data being transmitted to be stored or correlated.
Conformity: The protocols in the SIEM can be developed that automatically collect the necessary data to ensure compliance with corporate, organizational, or federal policies.
How Does SIEM Works?
The SIEM procedure is quite easy to follow. The whole process consists of four steps in main. The four stages are as follows:
The first stage is gathering information from various sources all over.
Then, it combines all the information to analyze it in real time.
SIEM solutions use rules and statistical correlations in order to generate the forensic investigation with actionable insights.
SIEM technology analyzes all information and categorizes threats based on their degree of risk to help security teams detect malicious hackers and reduce cyberattacks rapidly.
SIEM vs SOAR
Image Source: Medium
SIEM and SOAR collect security data from different sources; however, the sources and the amount of information they collect are distinct. While SIEM draws in various logs and event information from conventional infrastructure components, SOAR collects information from new threat intelligence feeds, endpoint security applications, and other third-party sources to give you an overall view of the security environment inside and outside the network.
When a SIEM issues the alert, it is left to the administrator to decide the course of the investigation. Contrarily, SOAR automates workflows for the investigation to start triaging and then apply remediation methods. SOAR starts at the point at which a SIEM’s capabilities stop. The two are in sync in the real world and best when used in conjunction.
| Capabilities | SIEM | SOAR |
| Security monitoring | Displays information through dashboards and embedded workflows for workloads, applications, as well as the entire security stack. | Receives alerts about malfunctions and initiates appropriate response and investigation procedures. |
| Generation of alerts | Automatically assesses and converts security signals into high-fidelity, actionable alerts dubbed Insights. | Gets alerts and insights from Cloud SIEM, or search specific alerts in real-time through Cloud SOAR daemons. |
| Analysis and treatment of false positives | Automated correlation of threat and enhancements using predictive Confidence Scores that help to reduce false positives by using crowdsourced Global Intelligence ML model. | Fully automated workflow, from alert validation through playbook activation. It creates incidents only when genuine dangers are discovered. |
The Role of SOAR in Advanced Threat Protection
“It takes approximately up to 45 minutes to investigate a phishing email. SOAR can speed up the process of security incident response by 10 times. In actual fact, SOAR can effectively reduce the negative impact of a breach on a company by as much as 96 percent.”
Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR) is the latest technology rapidly gaining popularity as a vital component of security operations across different industries. Companies use SOAR to monitor threats investigations and responses, security intelligence management, and complete SOC optimization. It can be extremely beneficial to increase efficiency within your current team and decrease the budget burden. SOAR is essential to Managed SOC and has become an integral element of cybersecurity.
It improves security operations against all types of cyber threats and cyber-attacks. It aids in solving the global challenges of cybersecurity for businesses to secure their information from security breaches. With the latest technological advancements incorporated, it makes security operations easier by managing and automating security tasks. Also, it assists in reducing the amount of time needed to deal with an incident and sending accurate and timely responses to identify threats.
SOAR helps companies assess cybersecurity threats immediately by adding security technology to enhance security overall and aids companies in avoiding security breaches in the initial instance. Nobody would ever want to risk their safety to combat the ever-growing cyber threat in a world based on data. It is crucial to obtain real-time alerts and reports on security incidents to avoid any security catastrophe and take proactive steps to stop any attack.
How SOAR Improves Efficiency and Effectiveness in Security Operations?
SOAR technology allows organizations to gather and combine huge quantities of security information and alerts from various sources. This facilitates the analysis of machine and human-led. It facilitates the standardization and automation of threat detection and recovery. SOAR technology can aid organizations in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations in the following ways:
Improves the speed of response to security incidents: SOAR tools can speed up the response time by integrating all tools that comprise the center’s security operation (SOC) arsenal, including threat intelligence sources, both external and internal, into the organization. Instead of relying on many different tools, security professionals can use a single data source to access all the information and indications of compromise quickly.
Facilitates the investigation process: In many instances, SOAR tools can look into low-level alarms and only escalate crucial alarms to security staff. Additionally, they offer an integrated view, which allows you to compare alarms generated by different tools and pinpoint the causes.
Minimizes the harm caused by attacks: Automation capabilities can help initiate action, like blocking an IP address or isolating a compromised system or endpoint. This can limit damage and give crucial information regarding the attack more quickly.
Reduces the time spent responding to false alarms: False positive alarms waste effort and security staff’s time, thus reducing their productivity. SOAR helps reduce false alarms.
Improves the effectiveness and efficiency of security and IT operations: SOAR integrates IT and cybersecurity operations to collaborate and give an overall view of the surrounding environment. It also improves the effectiveness and efficiency of security and IT operations.
Manages and prevents security threats: SOAR lets you capture knowledge to improve the capabilities of an organization to avoid and deal with security threats.
Provides meaningful and informative dashboards: SOAR offers these dashboards to ensure that businesses can comprehend and appreciate the work made by security teams.
Lowers the cost of operations: All aspects previously mentioned factors also reduce the operating costs.
Real-world Use Cases of SOAR
7 real-world use cases of SOAR include:
Phishing Attacks
With millions of phishing emails sent out daily, it should be no surprise that new and increasingly-damaging attacks are making headlines regularly. To aid businesses in this issue, SOAR detects emails that contain malware from shared inboxes, deletes Notify user IPs/URLs, and then investigates them with security intelligence. If the email attachment isn’t identified, it may be shared with the Sandbox for analysis.
Threat Hunting
In today’s threatening situation, more is needed just to be aware. Security indeed requires actively identifying and scouting for threats. SOAR automates the search for indicators for breach (IOC) against Intelligence on threats.
Insider Threat Detection
Negligent and malicious actions by insiders and attacks that use stolen credentials are the main cause of successful breaches. However, finding insider threats can be difficult for security operation teams. SOAR, therefore, incorporates multiple tools to speed up security threat identification and intervention.
Threat Intelligence
SOAR solutions can provide security teams with a fast and instantaneous method of making sure that their security infrastructure is using the most up-to-date information about threats at all times. With a precise and current understanding of IOCs, analysts can respond quickly to real threats, dramatically reducing MTTR and reducing risk.
Identify Verification/Enforcement
Rapid and easy authentication of privileged credentials is essential to maintain high-security hygiene. Security operations are required to allow easy access for legitimate users while safeguarding against the misuse or theft of credentials. SOAR aids in the automatic verification of user access rights for certain resources.
Endpoint Protection
Alerts related to endpoints can overwhelm security operations teams and delay prompt response. Utilizing security automation and orchestration, you can ensure that all alerts related to endpoints are dealt with. Actions to address and correct the issue can be carried out in real-time, which helps prevent incidents from becoming full-blown security breaches.
Forensic Investigation
SOAR platforms speed up investigations by automating data collection using different tools and establishing a central repository for all evidence collected. Integrated case management gives you easy access to all details of forensics needed to investigate quickly.
How SOAR Solutions Are Implemented in Security Operations?
Awareness of your SOAR requirements is the initial step in SOAR implementation. The next steps are about integrating SOAR into your existing procedures.
Identify Your Incident Response Workflows
Automation is among the main selling aspects of SOAR. But, you need to know what workflows can be designed and optimized for automation to get the advantages.
To begin, you need to map your response flow and determine the tasks that could be automated. They can be added as tasks within the SOAR system. Remember that if your workflow heavily depends upon manual entry and checking, you could completely overhaul the workflow and create it with the idea of automation in the back of your mind.
Begin with the most Automation-Friendly Tasks
Security responses are often slowed because of areas that demand human analysis. You should wait to automate these tasks. Instead, consider simple tasks such as the automation of basic alerts–essentially anything that doesn’t require much effort from your brain. Automate these first, and you’ll never be able to tell that you’re no longer doing these tasks manually.
Keep Researching
As cybersecurity threats are always evolving and evolving, so is the landscape of cybersecurity. Continue to research threat response best practices and discover how to incorporate them into playbooks and workflows. Change your procedures in light of past incidents. Always monitor the results of your incident response, and adjust accordingly.
Best Practices to Implement SOAR:
The SOAR toolset provides security professionals with the most efficient and effective procedure to make an order from chaos. Based on our extensive research, we’ve discovered that there are seven “best practice” categories that are essential to SOAR’s implementation.
Examine Organization & Capabilities
It isn’t possible to begin implementing a SOAR solution without understanding the requirements of your company as well as the extent that your company is committed to SOAR and the accessibility and capability of your employees. In order to do this, you must identify and manage the stakeholders and then gather staff members that are “DevSecOps” specialists.
Understand Scope
The notion of “scope” is an essential aspect of SOAR. The scope could refer to the geographical or size of a system as well as the structure of the system (that is, the platform upon which the system operates). This implies that “scope” will affect how you manage and implement the operation of a SOAR solution.
Apply Standards
Standards in cybersecurity are crucial, and with them, clarity may prevail. Regarding security, the notion of “standards” can refer to many things, from uniform naming conventions to setting the criteria that determine the success of an incident. Implementing a standardization procedure within SOAR can ensure efficient implementation and an effective response to an incident.
To do this, you must:
Establish Standards for definitions and names
Standardize your playbooks
Standardize integrations into systems
Develop scripting and coding standards
Set standards in line with your company’s Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
Standardize your documentation
Utilize CIM to streamline workflows
Clean Data
Data is the lowest point in the IT and security pyramid. It is the base that supports every other structure, platform, and application. Therefore, the integrity of data is crucial to use SOAR efficiently.
Know and Manage Your Workflow
Alongside ensuring that you adhere to the same guidelines when creating workflows, it’s crucial to be aware of your workflows both at the macro and micro levels.
Plan your Playbooks
Your workflows represent the most logical version of what you want your business to accomplish in the event of an incident. The Playbook will be your actual SOAR tool that can be used to capture all of your security procedures. Consistency between playbooks is crucial, as when you discover inconsistent playbooks you start to question all playbooks, so you should go back and conduct a full review of all the playbooks.
Monitor SOAR
SOAR is a “system made up of different systems.” It controls both output and input. The SOAR platform, in essence, can be described as a vast-scale system, meaning there are many avenues for things to be wrong. So, after you’ve implemented SOAR, continuous surveillance of the platform and its infrastructure is essential.
Conclusion: The Power of Automation and Orchestration in Cybersecurity
Automation and Orchestration in cybersecurity receiving recognition, praise, and experiencing rapid growth. Automation could save an organization 30 percent to 50% of its time and allow engineers and analysts to concentrate on more difficult tasks. This time could mean 100’s thousands of dollars in an entire year.
As time passes, increasing numbers of organizations will begin to implement more automation into their operations and begin to recognize software’s importance. With the many options available, start by understanding the fundamentals first.
Learn the five Ws for effective Security Orchestration Automation and Response implementation: Who (who are the most important individuals in the company who must be involved in the conversation), what (What Use Case(s) should be considered?) Where (where are assets information, applications, data, and individuals located within your system, and how will your process work with each of them) and when (when manual intervention is required to occur)? Why (why you’d like to automatize) and what (how can you achieve this? And how can we begin?).
Implementing such a program involves numerous moving parts, so be prepared today!
We hope this post helps you learn about Automation and Orchestration, What is Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR), What is Security Incident & Event Management (SIEM), The Role of SOAR in Advanced Threat Protection, How SOAR Improves Efficiency and Effectiveness in Security Operations, some Real-world Use Cases of SOAR, and finally the Power of Automation and Orchestration in Cybersecurity. Thanks for reading this post. Please share this post and help to secure the digital world. Visit our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium & Instagram, and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.