Table of Contents
Learn The Vulnerability Assessment Process With TheSecMaster- The Step-by-Step Guide
With limited time, money, and other resources, businesses responsible for protecting their IT systems must devise a plan to manage and stay ahead of cyber threats. It requires a balanced and effective vulnerability assessment process to ensure keeping the IT system’s vulnerability approach is feasible for their staff and doesn’t break the bank.
A vulnerability analysis systematically identifies possible security flaws in computer systems, networks, and software applications while ranking them in order of importance. The significance of this analysis rests in its capacity to provide your business with vital information, awareness, and comprehension of the risks. In all, running a vulnerability assessment process aims to enable responding appropriately to threats in its operating environment.
About Vulnerability Assessment Process
Business vulnerabilities may take various forms, but a common characteristic is potentially harming business data with severe consequences if left unaddressed. It keeps the door open to hackers, which can cause extensive harm. This requires businesses to effectively manage this risk by running a vulnerability assessment process.
Addressing security concerns requires adopting Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) plan that involves planning a thorough vulnerability assessment that helps businesses pinpoint security loopholes. It can help reduce the risk of exploitation by hackers. A key outcome of this cohesive strategy is a vulnerability report, which facilitates further preventive measures.
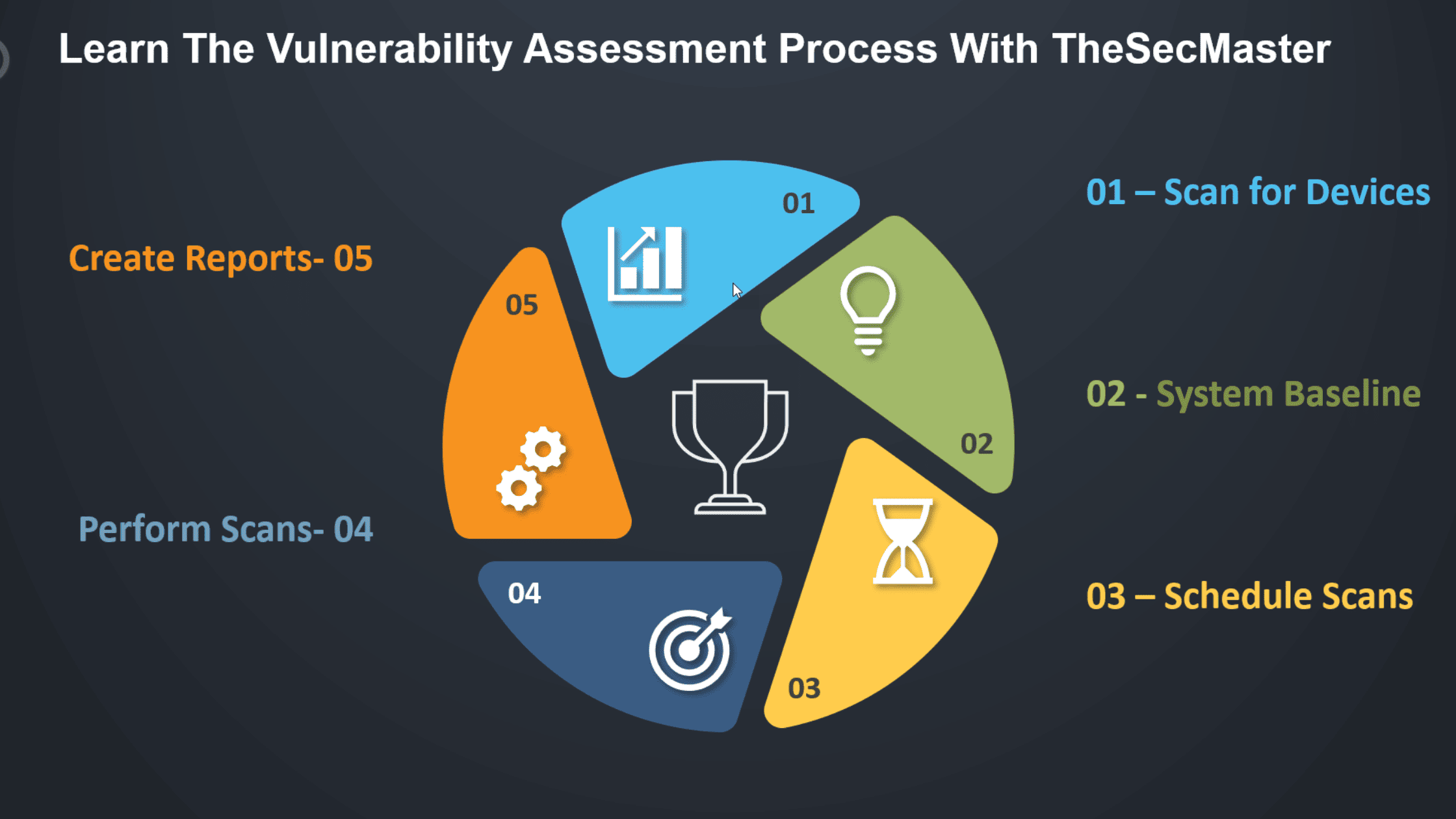
Let us now get through the vulnerability assessment process that can help identify potential security threats that ultimately enable safeguarding your business’ IT.
Step 1: Scan the Network to Discover Devices
Begin with thoroughly evaluating your network for potential security weaknesses. This is possible through meticulous manual checks or automated tools for scanning vulnerabilities. Although some scanner tools at the enterprise level may carry a high cost, you also have access to a wide array of free and open-source options that align with your organization’s needs.
Besides conducting the scan, businesses can leverage threat intelligence and vulnerability databases to identify vulnerabilities. These resources can help identify security defects and vulnerabilities while helping to reduce the number of false positives (incorrect warnings or false alarms indicating a security gap or suggesting harmful behavior).
Scanning for vulnerabilities requires identifying assets to be scanned. Typically, it includes assets like data, servers, systems, devices, and networks.
Next, prioritize assets that need to be secured by categorizing them into ‘high,’ ‘medium,’ and ‘low’ criticality. After that, define the scope and boundaries of the network, system, or application you plan to scan. It involves having legal and organizational permissions to assess vulnerability within the defined boundaries.
Lastly, document everything from the scope of scope asset scanning to including what systems will be scanned, types of vulnerabilities you look for, tools that will be used for scanning, etc.
Step 2: Define a System Baseline
This step in the vulnerability assessment process requires defining the system baseline, which requires analyzing and documenting the system’s or network’s baseline performance. That provides an idea of whether the existing systems are vulnerable to threats in the foreseeable future.
Evaluating the security vulnerabilities of a particular device requires ascertaining whether it complies with fundamental safety protocols. It needs gauging whether the configuration components mentioned below align with a standard benchmark:
The type of Operating System (OS) you will be using, including its specific edition, along with the applied service pack or build, where relevant.
Legitimized applications that are installed on devices running scans.
Compiling the list of services currently installed on the system and the required ports.
The presence of any open ports (which are not necessary) could serve as points of security compromise.
Defining a baseline system as a part of the vulnerability assessment process requires considering each device as a potential malicious actor. Therefore, performing a scan in the next step will help discover what an internal or external threat actor can access. Also, it helps compare such threat actors against known vulnerabilities and insecure configurations to simplify interpreting the scan results properly.
Augmenting the set of configuration parameters requires gathering supplementary data about the system, which includes incorporating system logs into a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) for analysis. Moreover, remaining aware of the potential weaknesses tied to the specific operating system, its version, installed applications, or active services can significantly help plan the system’s security.
Step 3: Configure the Scan
Businesses will have plenty of choices when picking up a vendor for vulnerability scanning services. But, setting up such a scan requires tackling the issue by outlining key goals and the specific system you choose to examine.
A scan configuration will require taking the following steps:
Identify the target IP address
The first step is to identify and input the IP addresses of the systems you wish to scrutinize as a part of vulnerability scanning. Since your target systems reside in these IP addresses, including them will ensure that the security scan considers it and looks for IP vulnerabilities.
Specify port range and protocol
Once the IP is registered, establish the range of ports to be scanned and decide on the protocol. This step further narrows down the scope of the scan, making it more efficient.
Mention scan targets
Next, it is necessary to indicate the type of target IP systems like databases, windows servers, applications, wireless devices, etc. You can enable more precise and relevant scan results by zeroing in on specific systems.
Determine scan parameters
Some common scan parameters here are aggressiveness, timing, and notifications. Ideally, determining the scan intensity can directly impact the performance of the systems that are being examined. Circumvent any potential disruption or downtime on these systems by scheduling the scan during off-peak or non-business hours.
Moreover, configure the system to alert you once the scan is completed. Such a proactive measure ensures you are kept abreast of the scan’s progress, allowing you to act on the results promptly.
Step 4: Perform the Scan
Once you decide on the type of scan to execute and have appropriately arranged the scan’s parameters, begin with running a scan. The time taken to complete the scan largely depends on how deep your target’s scope is and the degree of the scan’s invasiveness. Therefore, the process can range from a few minutes to several hours.
A network vulnerability scan can typically be categorized into three distinct stages:
Initial scanning: At this stage of the vulnerability assessment process, the scanning tool will attempt to “fingerprint” or identify the assigned targets to gather their fundamental details.
Target enumeration: With such information at its disposal, the tool moves on to the Target Enumeration stage, where it ascertains more intricate details, including active ports and services currently in operation.
Vulnerability identification: The final stage is vulnerability identification, where the scan leverages the garnered data, including service versions and configurations for each target IP. This data can accurately discern and map out any potential vulnerabilities that might be present within the target set.
Step 5: Create a vulnerability Assessment Report
After the scan, a dedicated unit will compile a comprehensive document delineating potential threats detected within all safeguarded resources. It should also be accompanied by a strategically designed scheme for their resolution.
Depending on the scan configurations, the document should focus on vulnerabilities that pose moderate to severe risks.
The document must also carry the details concerning:
the discovered susceptibility
the time of detecting vulnerability
the systems it potentially jeopardizes
the roadmap and necessary endeavors required to neutralize the threat.
Moreover, the security team should then furnish an empirical demonstration, termed a Proof of Concept (PoC) exploit, to exemplify how to manipulate each dangerous threat that can gain unauthorized access or disrupt services. Such a demonstration helps the stakeholders better understand each security flaw’s magnitude and implications, thereby underlining the importance of prompt remediation.
Wrapping up: Continuous Assessment is Key
Ultimately, conducting vulnerability assessments isn’t a one-off event but rather an ongoing task that requires frequent repetition. The driving factor behind this continuity is the relentless emergence of new vulnerabilities, coupled with regular updates and modifications to systems and software.
Regular security assessments offer constructive means to maintain a robust security stance, which is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of your organization’s cyber security strategy. The ultimate goal of undergoing a long vulnerability process is to identify potential weaknesses and convert those insights into stronger defenses that contribute to the success of your enterprise’s overall cyber resilience.
We hope this post helped you learn about the different stages of the Vulnerability Assessment Process. Thanks for reading this post. Please share this post and help to secure the digital world. Visit thesecmaster.com and our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, & Medium and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.