Table of Contents
What is DKIM? Why do we need DKIM? And How to create a DKIM record?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is one of the email authentication protocols which help to keep the integrity of an email, thus protecting users from a spoof, phishing, and other malicious activities.
In the previous articles, we discussed what email authentication is and one of the email authentication protocols Sender Policy Framework (SPF). This article gives a detailed view of what DKIM is and how to create a DKIM record for your organization.
What is DKIM?
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) is a technique used for email authentication, where the email is digitally signed by a cryptographic signature from the sender, which helps the receiving mail server to authenticate if it is from the legitimate sender. DKIM protects the recipient from being a victim of email attacks.
How Does DKIM Work?
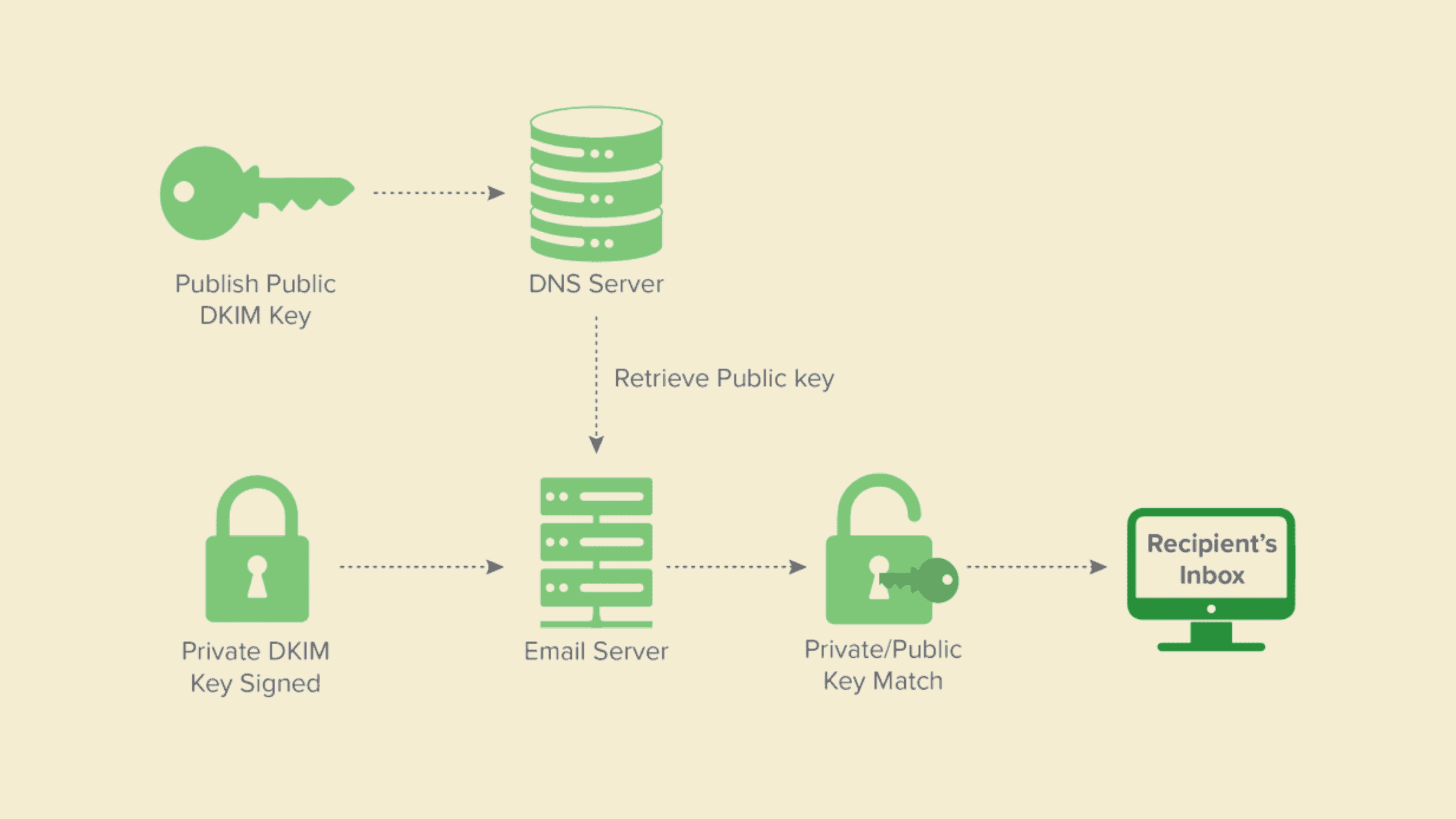
DKIM has a three-step process:
Identify which field we should add the DKIM signature to. It can be any field, including the ‘from’ address, the subject line, the content, and much more. The only condition is that the field should remain the same in transit, else the DKIM authentication won’t be successful.
Once the field is selected for the DKIM signature, the sender’s email platform will create a hash value of the text field selected for DKIM.
For example:
From: < Johndoe@abcdomain.com >Subject: DKIM TestConsider this will be mapped as a hash. 3003baf8986f930720abcfa607d81f53, once this hash is generated and encrypted with a private key, it will be only accessible by the sender.The third step is for the email gateway or the recipient mail server to find the public key that matches the private key, then the DKIM signature will be changed back to the original hash string by decrypting it.
After decrypting the DKIM signature to the original hash value, the recipient mailbox will generate its own hash for the field and compare it with the decrypted value.
The three-step process of DKIM (Credits: Dmarcian)
If the three processes are successfully completed, we can conclude two things. One is there was no change happened to the email while in transit. Two, the DKIM signer owns the mail.
What is a DKIM Signature?
DKIM signature is a unique cryptographic signature that does the validation of email. This hash is created using various fields in a mail, such as the body of the mail, subject, or any other part of the mail. Each time the hash generated will be unique as the fields for the hash are created when the message is sent, so it cannot be changed during further stages of sending the email.
The sender uses the private key of the domain to encrypt the email, and a hash is created. This creates the DKIM signature. The recipient server, upon receiving the mail, will encrypt the same fields of the message using the public key from the sender and creates a hash string. The recipient server then compares the hash value created with the decrypted sender’s hash. DKIM signature is considered to pass if both the hash values match, i.e., the DKIM validation is passed. A single change in the message will lead to a mismatch of hashes as the hash value created by encrypting with a public key will not match the hash value created by the sender’s mail server, which leads to DKIM failure.
DKIM validation guarantees the integrity of a mail is kept so that the recipient can be assured that it is from a legitimate source which in turn protects the user from being a victim of email compromise attacks.
How to Create DKIM Record?
To create a DKIM record, you should do this:
First, collect all the domains and the third-party services which send an email on your behalf. Request them to configure DKIM on their end, and a copy of the public key should be collected.
Second, the public/private key pairs should be generated. This can be done with the help of other third-party tools like Socketlabs, SparkPost or by open-source tools like opendkim.
What is DKIM Selector?
Just like SPF, a DKIM record is also a TXT record that is hosted in DNS; however, the recipient server should be able to find it amidst other TXT record entries.
The receiver mail server should be able to locate the public key of the domain. This is done with the help of the DKIM selector. The DKIM selector is essential since this public key is used to create the hash from the received mail and will be compared with the hash generated by the private key.
A DKIM signature header will be added to every mail sent if the DKIM is configured. The DKIM signature looks like this:
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa; c=relaxed/relaxed; d=myxyzdomain.com; s=s837fhs;
‘v’ indicates the version of DKIM‘a’ indicates the algorithm used for the hash‘c’ indicates Message canonicalization. The only valid tags are ‘simple’ or ‘relaxed.’‘d’ indicates the domain (primary) from where the message is sent.it is the Signing Domain Identifier (SDID)
The DKIM selector is indicated by the ‘s’ value. This value is generated along with the creation of public and private key pairs. We can test the DKIM selector by sending a mail to you after configuring DKIM.
Difference between DKIM and SPF
Both DKIM and SPF play an important role in email protection. While SPF saves the domain by preventing spoofed emails from using the sender domain, DKIM verifies that there is no data tampering done on an email by any third party.
SPF only ensures that the recipient will not receive spoofed emails from the sender, but it does not guarantee the detection of email tampering. Without DKIM, an attacker might send a tampered email to the recipient by hijacking it. So, SPF, along with DKIM, is necessary to protect the recipient from falling into such scams.
If the DKIM authentication fails, then DMARC comes into the picture. DMARC decides on what action should be taken on the emails which failed DKIM authentication. We will discuss this in detail on DMARC in our next post.
Conclusion
We all receive multiple emails in our day-to-day life. Organizations setting up DKIM records will save receivers from falling into malicious and scam emails, protecting their identity, money, and other sensitive information. Only configuring DKIM won’t do much of a favor. It should be combined with SPF and DMARC to protect from sophisticated cyber-attacks.
We hope this post helps you understand what is DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), Why do we need DKIM, and how to create a DKIM record. Please share this post and help to secure the digital world. Visit our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium & Instagram, and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
Aroma Rose Reji
Aroma is a cybersecurity professional with more than four years of experience in the industry. She has a strong background in detecting and defending cyber-attacks and possesses multiple global certifications like eCTHPv2, CEH, and CTIA. She is a pet lover and, in her free time, enjoys spending time with her cat, cooking, and traveling. You can connect with her on LinkedIn.