Table of Contents
What is DMARC? How DMARC Works? How to Create DMARC Record? And What are the Benefits of DMARC?
Anyone looking to protect their emails from attackers will be familiar with the email authentication protocols. In previous posts, we discussed the mail two email authentication protocols SPF (sender policy framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). DMARC sits on top of SPF and DKIM and uses these policies for further verification of email.
In this article, we will discuss what is DMARC, how DMARC works, How to create a DMARC record, and what are the benefits of DMARC in detail.
What is DMARC?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, or DMARC, is an email authentication policy that delivers protection on the domain level of the email channel. DMARC sits on top of the already existing authentication protocol SPF and DKIM. It helps the domain owners to define how to configure their domain against scams and what action needs to be taken if the SPF and DKIM authentication fails. DMARC provides an additional layer of email security to the business from attackers impersonating and sending mail on behalf of the legitimate domain.
DMARC is a great help to Internet service providers (ISPs) as it identifies the spammers and blacklisted content and prevents them from invading the inbox. This help in reducing false positives and provides an impression on ISPs in the market.
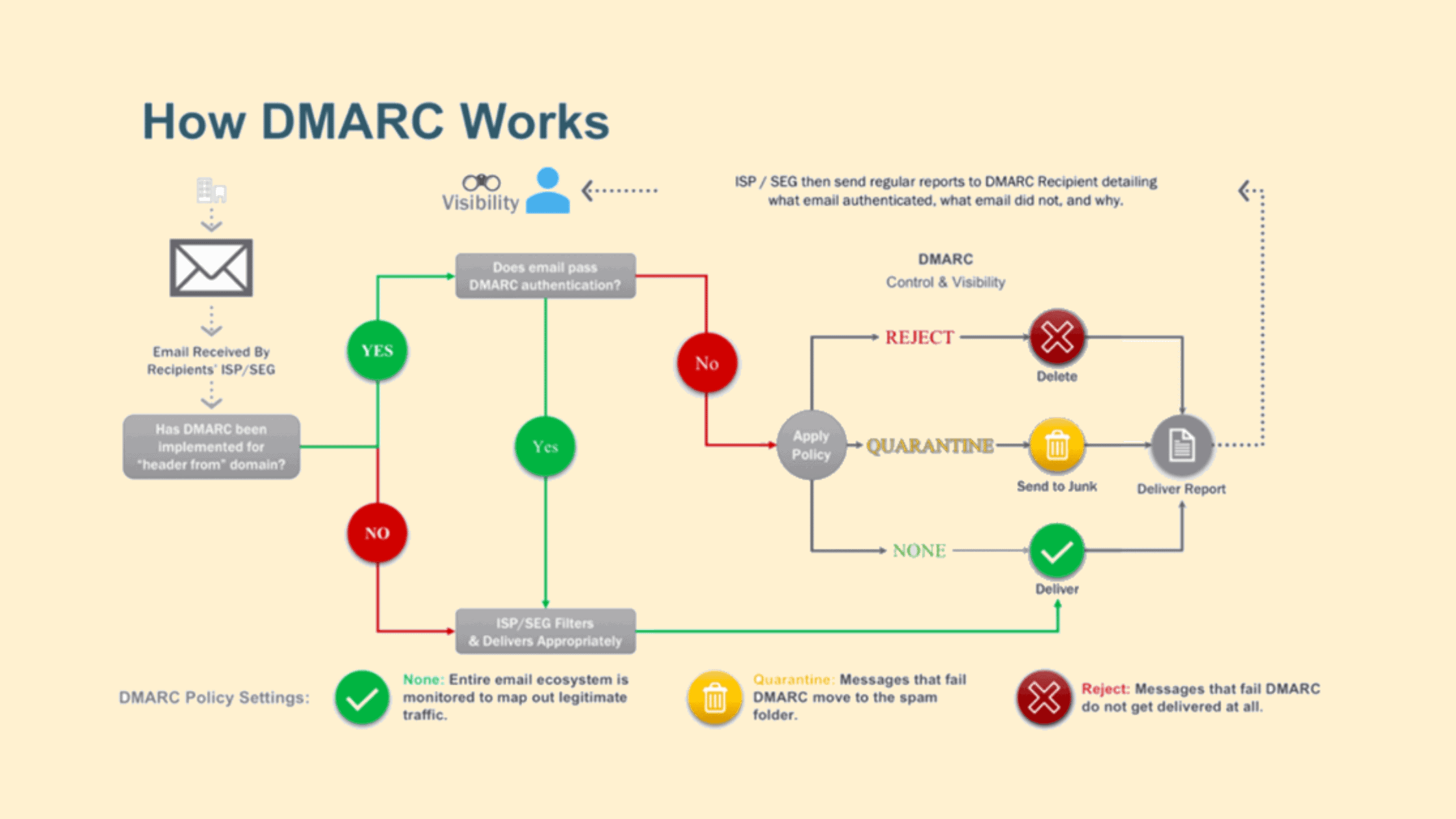
How DMARC works?
DMARC cannot be implemented on its own; it only works only if either or both SPF and DKIM is implemented. A male can pass DMARC authentication only if it passes SPF authentication and/or DKIM authentication. The Sender can configure what to do with an email if it fails the DMARC authentication. This is established by defining DMARC policy by the domain owner. There are three DMARC policy they are
‘none’ – This policy only monitors the traffic and delivers all messages to the receiver mailbox but sends a report to the domain owner mentioned in the ‘mailto:’ of the DMARC record.
‘quarantine’ – If the mail fails the authentication, it will be sent to the receiver’s spam folder.
‘reject’ – message will not be delivered if it is unauthorized.
Image source: Proofpoint
During the initial authentication setup time, the ‘none’ policy is good as the domain owner can validate what traffic is happening and whether all legitimate communication is authenticating properly. The DMARC report received can be analyzed, and it will help a lot in understanding the legitimate emails and other traffics, if any. Once the domain owner is ready with all the details of third-party services used and fixed all authentication issues, if any, they can configure the DMARC policy to ‘reject.’ This will protect you from business email compromise attacks, phishing scams, and other email attacks.
How to Create DMARC record?
Just like SPF and DKIM records, the DMARC record is also hosted on the domain’s DNS as a TXT record. Creating a DMARC record can be different based on the domain registrar, or the host DNS record is the same.
The first step is to create a TXT record and also enter a name and value for the record. Name the record as DMARC. If the domain is not appended as it happens in some cases, name the record manually as _dmarc.yourdomainname.com
Enter the record value, The DMARC value looks like
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=\ ; ruf=\; pct=100
‘v’ indicates the version of DMARC, it will be same for all records
‘p’ indicates what policy should be applied if the DMARC authentication pass or fail
‘rua’ indicates that the aggregated report will be sent to the mentioned mailbox
‘ruf’ is the mailbox where the forensic reports will be shared
‘pct’ indicates the percentage of emails to the policy that should be applied. This is determined by the domain owner.
There are two types of reports shared by DMARC aggregated reports and forensic reports.
Aggregated reports are XML documents that are designed to be machine-readable. These reports provide statistical data on all the emails that are received in the name of the legitimate domain, the message disposition, and the date received.
Forensic reports are enclosed in a special format known as AFRF, where any DMARC failed message copy will be shared individually. This will be very helpful for forensic analysis, troubleshooting authentication errors, and also finding imposter malicious domains over the internet.
What is DMARC Domain Alignment?
Domain alignment is a part of the DMARC validation and compliance process, which requires SPF and DKIM to meet a few conditions.
For Domain alignment of SPF, the ‘from’ of the message and the ‘Return-path’ of the mail should be the same.
For DKIM’s domain alignment, the ‘from’ of the message and ‘d=domain’ in the DKIM signature should match.
This alignment can be strict or relaxed based on the domain owner’s requirements. This can be mentioned in DMARC policy while creating it.
What are the benefits of DMARC?
Implementing DMARC gives multiple benefits to the domain owner.
VISIBILITY: They decrease false positive messages and increase reliability. DMARC provides more visibility on what all emails are received by users from your domain through the aggregated and forensic reports shared.
REPUTATION: DMARC improves brand reputation by saving customers from falling into fraudulent activities targeted by mail.
SECURITY: DMARC increases the trust of customers since no illegitimate mail will be allowed to the user if the policy is strictly enabled.
There are so many benefits to implementing all authentication policies correctly. The SPF, DKIM, and DMARC together can do a great deal in catching scammers who spoof the identity of legitimate domains.
I hope this post helped in understanding what is DMARC, how DMARC works, How to create a DMARC record, and what are the benefits of DMARC in detail. Thanks for reading this post. Please share this post and help to secure the digital world. Visit our social media page on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium & Instagram, and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
Aroma Rose Reji
Aroma is a cybersecurity professional with more than four years of experience in the industry. She has a strong background in detecting and defending cyber-attacks and possesses multiple global certifications like eCTHPv2, CEH, and CTIA. She is a pet lover and, in her free time, enjoys spending time with her cat, cooking, and traveling. You can connect with her on LinkedIn.