Table of Contents
What is New in KB5034763? How to Download and Install Windows 10 build 19044.4046 and 19045.4046?
On February 13, 2024, Microsoft released its latest monthly cumulative update for Windows 10- KB5034763. This crucial update is now available for Windows 10 versions 21H2 and 22H2, bringing these versions to builds 19044.4046 and 19045.4046 respectively upon installation.
The KB5034763 update contains a wide range of bug fixes, security enhancements, and some exciting new features. Most noticeably, Microsoft has added an interactive weather panel to the Windows 10 lock screen which shows expanded forecast details on hover and opens a full weather report on click. Additionally, changes have been made to comply with Europe's Digital Markets Act regulations by March 6.
This update serves as the latest monthly "Patch Tuesday" release which rolls up security patches, system improvements, and new features into a single cumulative update. Installling each month's cumulative update is vital for remaining secure and up-to-date with the Windows ecosystem.
In this blog post, we will cover the essential details surrounding KB5034763 including what's new, a look at supported versions, step-by-step instructions for manually downloading and installing the update, best practices for post-update system cleanup, directions for uninstalling or hiding the update if desired, and more. Stay tuned for a comprehensive look at this month's cumulative patch for Windows!
Update for Windows 11 users: Microsoft has published KB5034765 for Windows 11. Visit this page to learn what is there in the KB5034765 update.
What are Latest Cumulative Updates (LCU)?
Microsoft introduced monthly cumulative updates for Windows 10 back in 2016 with the "Windows as a Service" model. These updates roll up all fixes for the month into a single cumulative update package.
Latest cumulative updates (LCU) provide the following benefits:
Deliver both security and non-security fixes published that month
Contains improvements to reliability and performance
Introduces new features and enhancements
Replaces any previous monthly updates
Microsoft releases LCU updates on Patch Tuesday, which falls on the second Tuesday of each month. They are then revised over the following weeks to address any issues. LCU updates build incrementally on previous updates.
Why You Shouldn't Miss Cumulative Updates?
Here are key reasons it's vital to promptly install the latest cumulative updates:
Critical for staying secure - Fixes security vulnerabilities used in attacks
Resolve system issues - Repairs bugs causing crashes or glitches
Performance improvements - Speeds up boot time and overall efficiency
Additional capabilities - New features and options added over time
Future update requirements - Later updates depend on previous patches
Support contingent on updating - Microsoft support requires staying current
Overall, monthly cumulative updates form a "rolling baseline" of fixes and improvements for Windows 10. Skipping them puts your security, stability, and Microsoft support at risk across both short and long-term.
Windows 10 Latest Builds and Their End of Support
The KB5034763 cumulative update is available for Windows 10 versions 21H2 and 22H2. By installing this latest patch, devices running Windows 10 21H2 will transition to build 19044.4046. While Windows 10 22H2 devices will shift to build 19045.4046.
In addition to the actively updated versions, Microsoft also provides ongoing support for several older Windows 10 LTSC/LTSB editions. The latest builds for these long-term support channel versions are:
Windows 10 1809 (LTSC) - Build 17763.5458
Windows 10 1607 (LTSB) - Build 14393.6709
Windows 10 1507 (LTSB) - Build 10240.20469
Check out the table below for a full breakdown of the various Windows 10 LTSC/LTSB versions along with their latest patch release dates, build numbers, and end of support timelines:
Servicing channels
|
Version
|
Servicing option
|
Availability date
|
Latest revision date
|
Latest build
|
End of servicing: Home, Pro, Pro Education and Pro for Workstations
|
End of servicing: Enterprise, Education, IoT Enterprise, and Enterprise multi-session
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
22H2
|
General Availability Channel
|
2022-10-18
|
2024-02-13
|
19045.4046
|
2025-10-14
|
2025-10-14
|
|
21H2
|
General Availability Channel
|
2021-11-16
|
2024-02-13
|
19044.4046
|
End of servicing
|
2024-06-11
|
Enterprise and IoT Enterprise LTSB/LTSC editions
|
Version
|
Servicing option
|
Availability date
|
Latest revision date
|
Latest build
|
Mainstream support end date
|
Extended support end date
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
21H2
|
Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC)
|
2021-11-16
|
2024-02-13
|
19044.4046
|
2027-01-12
|
2032-01-13 (IoT Enterprise only)1
|
|
1809
|
Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC)
|
2018-11-13
|
2024-02-13
|
17763.5458
|
End of servicing
|
2029-01-09
|
|
1607
|
Long-Term Servicing Branch (LTSB)
|
2016-08-02
|
2024-02-13
|
14393.6709
|
End of servicing
|
2026-10-13
|
|
1507 (RTM)
|
Long-Term Servicing Branch (LTSB)
|
2015-07-29
|
2024-02-13
|
10240.20469
|
End of servicing
|
2025-10-14
|
With mainstream support ending in January 2027, Windows 10 21H2 LTSC is recommended for most business/enterprise that require an enduring platform. However, for devices with a 10+ year lifecycle, the IoT Enterprise edition extends support for version 21H2 until January 2032.
This table provides a helpful guide for identifying your Windows 10 build version and channels to determine upcoming end of support dates. Confirm your specific Windows runtime version and channel in Settings > System > About.
Verify the Version of Windows Your PC is Running
Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
Type winver into the box and press Enter. This will display the version of Windows your computer is running.
View Installed Updates in Programs and Features from the Control Panel
You can view the installed Windows Updates on your Windows 10 device through the Programs and Features settings:
Open the Start Menu and search for “Control Panel“. Click to open the desktop app.
In the Control Panel, click on the “Programs and Features” option.
On the left pane, click on the “View installed updates” link. This will display a list of all updates installed on your PC.
To check if a specific update is installed, use the search box in the top right corner. Enter the Knowledge Base (KB) number of the update, for example KB5034763.
As you type, the list filters to match the entered text. If the update shows up in search results, that confirms it is present on your system.
Select the update from the list to further expand and view detailed information about it – description, installation date, update type, and more.
What is New in KB5034763- February 2024 Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 22H2 and 21H2?
The February 2024 patch KB5034763 delivers a range of security fixes, system enhancements, and new features for Windows 10 versions 21H2 and 22H2.
Most noticeably, Microsoft has introduced a new interactive weather experience on the default lock screen which shows expanded forecast details on hover and opens a full weather report from MSN when clicked. This provides a handy way to quickly check the weather without signing in.
Additionally, Microsoft continues rolling out changes to comply with Europe's Digital Markets Act regulations by March 6th, 2024. This includes ensuring Windows honors your default browser choice rather than forcing Microsoft Edge for specific links.
Beyond the highlights, KB5034763 provides a swath of general improvements including:
Security updates for over 70 documented vulnerabilities
Bug fixes for issues with Remote Desktop, BitLocker, app launching, and more
Increased reliability of startup, networking, and group policy handling
Smooth reconnection to previous Remote Desktop sessions
More seamless keyboard language hot switching in RemoteApps
Proper synchronization of date/time zones in Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Better deletion of cloud files and optimization of disk space
Resolutions for some printer configurations being wrongly set up as scanners
Blocks the persistent return of removed Internet Explorer shortcuts
As is standard for monthly cumulative updates, KB5034763 focuses mainly on security hardening, bug fixes, performance improvements, and seamless integration of previous patches. However, the new lock screen widget introduces helpful at-a-glance weather visibility.
How to Download and Install KB5034763 on Windows 10?
Most Windows 10 devices will automatically download and install the latest KB5034763 cumulative update from Windows Update. However, you can manually download and install the update as well through the Microsoft Update Catalog if desired.
Here are the step-by-step directions for both installation methods:
Method 1: Install KB5034763 via Windows Update
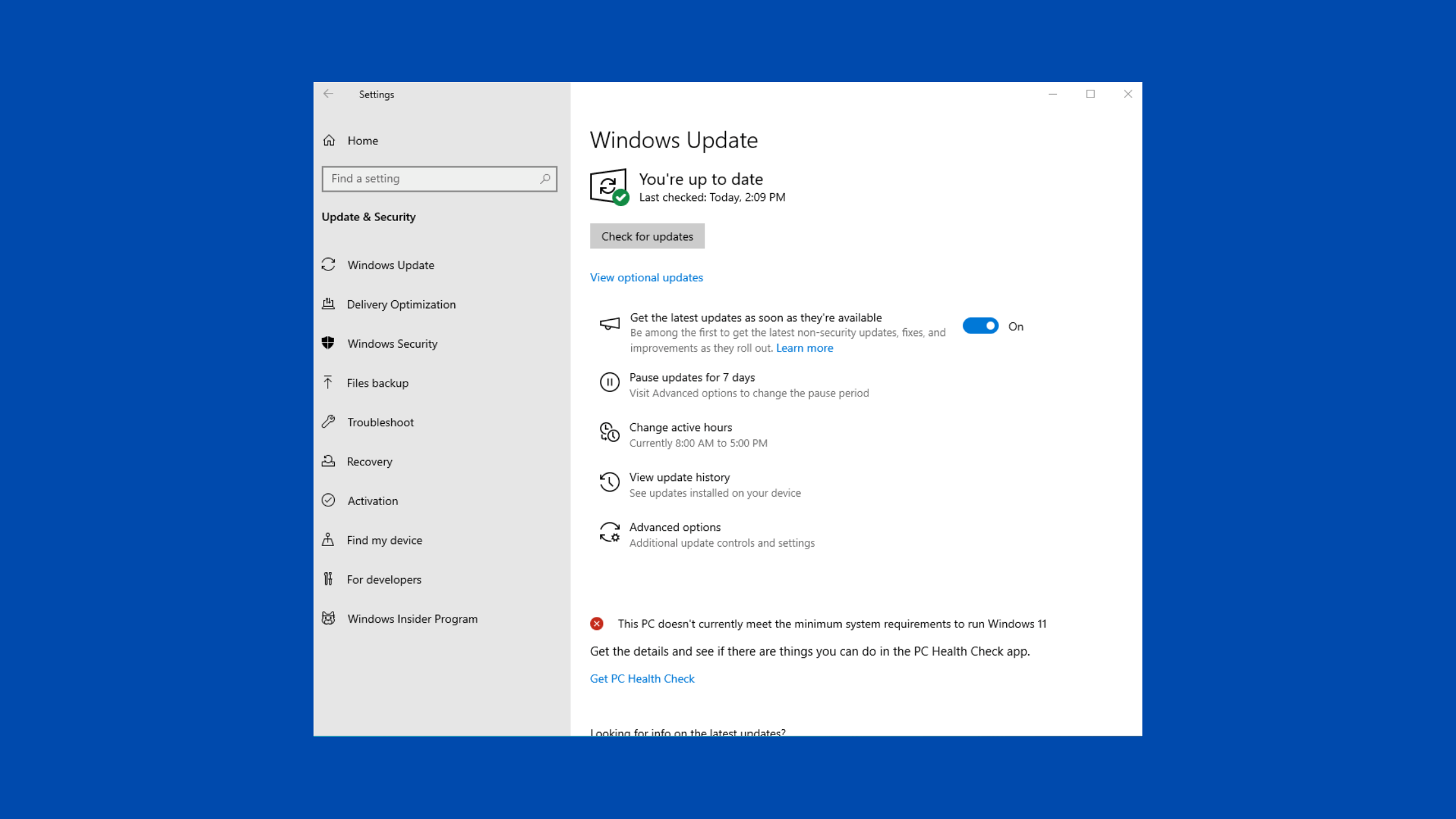
Open Settings and go to Update & Security > Windows Update.
Click on Check for updates. Windows will search for the latest available updates for your version.
Once KB5034763 is found, click Download and install.
Schedule a restart time to complete the installation if prompted.
After restarting your computer, Windows 10 is now updated to the latest cumulative update.
Method 2: Manually install KB5034763 from Microsoft Update Catalog
Visit the Microsoft Update Catalog website and search for KB5034763.
Select Download next to the update listing and save the
.msuinstaller file.Once downloaded, double click the MSU file to launch the installer.
Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the standalone installation.
Restart your device when prompted to finish updating Windows 10.
These methods allow you to install the latest January 2024 fixes and enhancements on your Windows 10 device. For enterprise deployment, tools like WSUS or SCCM can be used.
You can manually download the standalone installer for your version of Windows 10:
For other Windows 10 builds, visit Microsoft Update Catalog page and search the KB on the search box.
Note: It’s important to thoroughly test cumulative updates in a non-production environment before deploying them in a live production environment to ensure compatibility and avoid any unexpected issues.
Following either method, the entire KB5034763 install process takes just a few minutes. After your computer reboots, you will be running the latest Windows 10 21H2 or 22H2 cumulative update.
System Cleanup After the Installation of Windows Updates
To perform a cleanup after installing Windows updates, you can run the following commands sequentially in Command Prompt with administrative privileges:
Open Command Prompt with administrative privileges: Right-click on the Start button, and select “Command Prompt (Admin)” or “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” to launch the Command Prompt with administrative rights.
#1. Run the command to analyze the component store:
dism.exe /Online /Cleanup-IThis command analyzes the component store and provides a report on the size of the component store and the potential disk space savings that can be achieved by running cleanup operations.
#2. Run the cleanup commands:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanupThis command cleans up the superseded and unused system components from the Windows Update repository. It helps to reclaim disk space by removing unnecessary files.
#3. Perform a Windows Update cleanup:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup /ResetBaseThis command combines the functionality of the previous command with an additional step that removes all superseded versions of every component in the component store. This action cannot be undone, so it’s important to ensure you have all the necessary updates installed and your system is stable before proceeding.
#4. Remove temporary files:
cleanmgr.exe /verylowdiskThis command opens the Disk Cleanup utility, which allows you to remove various temporary files, including Windows Update temporary files, downloaded program files, and more. It presents you with a list of file categories that you can select to clean up. Choose the desired categories and click “OK” to remove the temporary files.
By running these commands, you can free up disk space by removing unnecessary Windows Update files and temporary files generated during the update process. Remember to exercise caution when using these commands and ensure your system is in a stable state before proceeding.
Uninstalling the KB5034763 Update
If you encounter issues after installing the KB5034763 update on Windows 10, you can uninstall it to revert back using the following methods:
Using Control Panel
Open the Control Panel on your computer.
Click on the Programs and Features option.
On the left pane, click on View installed updates.
In the list, locate and select the KB5034763 update under the Microsoft Windows section.
Right click on it and click Uninstall.
Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the uninstallation process.
Using Command Line
Search for Command Prompt, right click and select Run as administrator.
Run the command:
wusa /uninstall /kb:5034763Restart your computer when prompted to finish uninstalling the February 2024 cumulative update.
These steps will restore your Windows 10 device to the previous version, before you installed the KB5034763 update.
Block KB5034763 Update from Being Installed
You can temporarily block the installation of the latest KB5034763 cumulative update on your Windows 10 computer using the following steps:
Download the Windows Update Blocker (WUB) tool.
Run the wub.exe file and select “Hide Updates” option.
Check the box next to KB5034763 update and click Next.
Click Close once the blocking is completed.
This will add a registry key to prevent Windows Update from automatically downloading or installing KB5034763. You can uninstall the blocker tool later on when ready to install the February 2024 cumulative update.
For enterprise environments, blocking can also be configured through Group Policy, SCCM, WSUS, or other centralized management tools as per organizational update management policies.
Bottom Line
The Windows 10 February 2024 KB5034763 cumulative update delivers security enhancements and fixes for numerous bugs affecting system stability, performance, and usability. Most notably, it adds a new interactive weather panel to the lock screen.
We recommend promptly installing the latest updates using either Windows Update or the Microsoft Update Catalog. Cumulative updates keep Windows 10 protected and running smoothly. However, you can uninstall or hide problematic updates if they cause issues after installing.
Hope you found this summary of what's new in KB5034763 helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions. Visit our website, thesecmaster.com, and social media pages on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, & Medium and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
What is New in KB5034122? How to Download and Install Windows 10 build 19044.3930 and 19045.3930?
What is New in KB5031356 And How to Download and Install Windows 10 build 19045.3570?
What is New in KB5028166, a Cumulative Update for Windows 10 Version 22H2 and 21H2?
What is New in KB5034123? How to Download and Install Windows 11 build 22621.3007 and 22631.3007?
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.