Table of Contents
What Is New in Kali Linux 2024.4? And, How to Upgrade Kali Linux to 2024.4 From Older Release?
Offensive Security has released the fourth and final release of its flagship Linux distribution, Kali Linux, for 2024. The company announced Kali Linux 2024.4 on December 16, 2024, bringing significant changes to the platform. As with previous releases, this update introduces several important changes that cybersecurity professionals and ethical hackers should explore. One of the most notable changes is the transition to Python 3.12 as the default Python version, marking a significant shift in how Python packages are managed. The release also says goodbye to i386 architecture support, streamlines the Raspberry Pi installation process through the official Raspberry Pi Imager, and brings important updates to Kali NetHunter.
We created this post to help our thesecmaster.com readers understand what's new in Kali Linux 2024.4, why upgrading to this version is important, what security professionals and ethical hackers can expect from this release, and how to upgrade their existing Kali Linux installation to 2024.4. We'll break down each of these topics one by one, providing clear and detailed information about the latest improvements and changes in this final release of 2024.
The transition to Python 3.12 and the retirement of i386 architecture support represent significant changes in how Kali Linux evolves to meet modern cybersecurity needs. Whether you're a seasoned penetration tester, a cybersecurity researcher, or someone learning ethical hacking, these updates will impact how you use Kali Linux for security testing and assessment. Let's explore these changes in detail without further delay.
Importance of Kali Linux in Cybersecurity Community
Kali Linux has established itself as the cornerstone operating system in the cybersecurity community, particularly among penetration testers, security researchers, and ethical hackers. Its dominance in the field stems from its laser-focused approach to security testing and the comprehensive suite of cybersecurity tools it offers right after installation.
As a Debian-based open-source distribution maintained by Offensive Security, Kali Linux continues to evolve with the changing landscape of cybersecurity. The 2024.4 release demonstrates this evolution with its transition to Python 3.12 and modern architecture support, ensuring that security professionals have access to the latest and most efficient tools. The distribution comes preinstalled with over 600 specialized tools, each serving specific purposes in penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, digital forensics, network analysis, and security auditing.
What sets Kali Linux apart from general-purpose distributions is its clear mission and specialized focus. The platform is designed specifically for security professionals to:
Conduct thorough security assessments and penetration tests
Perform advanced vulnerability research and exploitation
Carry out detailed digital forensics investigations
Execute comprehensive network security audits
Practice and develop ethical hacking skills in a controlled environment
In essence, Kali Linux's unwavering focus on security testing, combined with its professional maintenance, comprehensive toolset, and strong community support, continues to make it the definitive choice for cybersecurity professionals. Its role in shaping the future of security testing and ethical hacking remains as crucial as ever, especially as we face increasingly sophisticated cyber threats and security challenges.
What Is New in Kali Linux 2024.4?
If you've been following Kali Linux's development, this post will help you understand the significant changes introduced in Kali 2024.4. For newcomers to Kali Linux, while some concepts might seem complex, we'll break down everything to ensure you understand what this release brings to the table.
Let's dive right in. Kali Linux 2024.4 was released on December 16, 2024, marking the final release of the year. This version brings substantial changes to the core system architecture and tools, focusing on modernizing the platform and improving the user experience. While it may not be considered a milestone release, 2024.4 introduces several important changes that security professionals should be aware of.
Key Highlights in this release since the September 2024.3 release:
14 new hacking tools were added including enumeration, intelligence gathering, and post-exploitation tools
Python 3.12 as Default: Python 3.12 replaces older versions, with pipx now managing Python tools for better isolation.
End of i386 Support: 32-bit architecture has been deprecated, aligning with modern 64-bit systems.
Enhanced Raspberry Pi Imager Support: Users can now apply customizations directly from the Raspberry Pi Imager tool.
NetHunter Updates:
Wifipumpkin3 replaces the Mana toolkit for creating fake APs with working internet.
A new Kernel tab allows direct kernel flashing from the app.
Improved installer with full Magisk support and command-line installations.
Updated support for 100 devices, including the first Android 15 device.
6. Kali ARM SBC Updates:
Raspberry Pi 5 gains KMS-enabled graphics and improved auto-detection for DSI displays and cameras.
Support added for devices like Raspberry Pi 500, Gateworks Newport, USB Armory MKII, and BeagleBone Black.
7. Miscellaneous Improvements:
Updated documentation with new NetHunter guides and pipx usage.
Desktop fixes: XFCE4 no longer needs
xcape, and GNOME text editor syntax highlighting is improved.Console character map defaults to UTF-8 to fix corrupt character issues.
Jim O’Gorman’s SINCON 2024 talk is now publicly available.
New Tools Added in Kali Linux 2024.4
According to the the Kali’s official article, Kali Linux 2024.4 has been shipped with 14 new tools. They are:
bloodyad - Active Directory privilege escalation framework (Submitted by @Arszilla)
certi - Ask for certificates to ADCS and discover templates (Submitted by @Arszilla)
chainsaw - Rapidly search and hunt through Windows forensic artefacts (Submitted by @Arszilla)
findomain - Fastest and most complete solution for domain recognition (Submitted by @Arszilla)
hexwalk - Hex analyzer, editor and viewer
linkedin2username - Generate username lists for companies on LinkedIn
mssqlpwner - Interact and pwn MSSQL servers
openssh-ssh1 - Secure SHell (SSH) client for legacy SSH1 protocol
proximoth - Control frame attack vulnerability detection tool (Submitted by @TechnicalUserX)
python-pipx - Execute binaries from Python packages in isolated environments
sara - RouterOS Security Inspector (Submitted by @casterbyte)
web-cache-vulnerability-scanner - Go-based CLI tool for testing for web cache poisoning (Submitted by @Arszilla)
xsrfprobe - An advanced Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF) audit and exploitation toolkit.
zenmap - The Network Mapper (nmap) front end (
zenmap-kbxis no longer needed!)
Python 3.12 as the New Default Version
One of the most significant updates in Kali Linux 2024.4 is the introduction of Python 3.12 as the default version. This shift marks a major milestone for the platform, reflecting its commitment to staying aligned with the latest advancements in software development. Python, being a cornerstone of many penetration testing and automation tools, plays a critical role in the Kali Linux ecosystem, and this update ensures that users benefit from the latest features, improvements, and optimizations.
Key Changes with Python 3.12
Deprecation of Older Versions: With Python 3.12 as the default, older Python versions are now deprecated, ensuring the operating system remains forward-compatible and secure.
Transition from pip to pipx: Kali Linux has replaced the traditional
pippackage manager withpipxfor Python-based tools. Unlikepip, which installs packages globally or in isolated virtual environments,pipxallows tools to run in isolated environments automatically. This reduces dependency conflicts and makes it easier to manage Python applications without altering the system configuration.
For cybersecurity professionals, this update ensures that Python-based tools included in Kali Linux, such as Metasploit and Empire, are future-proofed against upcoming changes in the Python ecosystem. It also enables developers to build and test new tools using the latest Python standards without worrying about compatibility issues. The transition to pipx simplifies managing Python tools, especially in complex penetration testing environments where dependency conflicts can be a frequent challenge.
Goodbye to i386 Architecture
With the release of Kali Linux 2024.4, the longstanding support for the i386 (32-bit) architecture has officially ended. This marks a significant milestone in Kali’s evolution, reflecting the global trend of transitioning towards more modern and efficient 64-bit systems. While this decision may affect users still relying on older hardware, it aligns with the broader focus on performance, security, and resource optimization.
Why the End of i386 Support?
The discontinuation of i386 support is driven by several key factors:
Modernization of Infrastructure: Most modern hardware, including processors and systems, now fully supports 64-bit architecture, offering enhanced performance and capabilities.
Improved Security: 64-bit systems benefit from advanced security features like Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) and Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR), which are less effective on 32-bit architectures.
Optimized Resource Utilization: 64-bit systems are better suited for handling larger memory spaces and multitasking, making them ideal for resource-intensive penetration testing tools and frameworks.
Simplification of Development: Dropping i386 simplifies the maintenance and development process for the Kali Linux team, allowing them to focus on modern hardware and software innovations.
Users running Kali Linux on legacy 32-bit systems will no longer receive updates, support, or new features. This could pose a challenge for those with older hardware or environments that exclusively rely on 32-bit architecture. However, it’s worth noting that 32-bit compatibility layers are still available in some cases, enabling partial functionality for outdated applications or environments.
Deprecations in the SSH Client: DSA Keys
Kali Linux 2024.4 introduces an important security enhancement by deprecating DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) keys in the SSH client. This update reflects a broader effort to ensure the use of secure and modern cryptographic algorithms across the platform, keeping up with the latest security best practices.
Why DSA Keys Are Deprecated?
DSA keys, while widely used in the past, have several critical limitations that make them unsuitable for modern cryptographic environments:
Weak Security Standards: DSA keys are limited to a 1024-bit key size, which is no longer considered secure by current cryptographic standards.
Reliance on RNG: DSA keys depend heavily on random number generators (RNG) for their operation. Any weakness or predictability in the RNG can compromise the security of the key.
Better Alternatives Available: Modern algorithms like RSA, ECDSA, and Ed25519 offer stronger security, better performance, and broader adoption across tools and platforms.
By deprecating DSA keys, Kali Linux ensures that users default to more secure cryptographic methods, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities during SSH communications.
Enhanced Raspberry Pi Imager Support
With the release of Kali Linux 2024.4, users can now apply customizations directly from the Raspberry Pi Imager software when creating bootable images for Raspberry Pi devices. This improvement simplifies the setup process, allowing users to configure settings like hostname, SSH keys, and network preferences before writing the image to an SD card or USB drive.
This feature saves time and effort, particularly for professionals deploying Kali Linux on multiple Raspberry Pi devices for penetration testing or portable security labs. By enabling preconfigured customizations, users can streamline workflows and focus more on their tasks rather than manual post-setup configurations.
To use this feature:
Launch the Raspberry Pi Imager tool.
Choose the Kali Linux ARM image as the operating system.
Apply customizations using the built-in configuration options (e.g., hostname, SSH settings).
Write the image to your SD card or USB drive.
This update makes deploying Kali Linux on Raspberry Pi even more efficient and user-friendly, especially for Raspberry Pi 5 users looking to leverage the latest hardware advancements.
Updates on NetHunter
With the release of Kali Linux 2024.4, Kali NetHunter, the mobile penetration testing platform, receives substantial updates across its app, store, installer, website, and kernel/device support. These enhancements solidify NetHunter's position as a powerful tool for cybersecurity professionals on Android devices, making mobile testing more accessible and efficient than ever before. Let’s delve into the details of these updates:
NetHunter App Enhancements
The NetHunter app introduces two significant features in this release:
Wifipumpkin3 as Mana Toolkit Replacement: The aging Mana Toolkit has been replaced with Wifipumpkin3, thanks to groundbreaking research by @yesimxev. This tool allows users to create a fake access point (AP) with working internet, even over mobile networks. This enhancement expands penetration testing capabilities directly on Android devices.
Kernel Flashing from the App: A new Kernel tab has been added to the NetHunter app, enabling users to flash kernels directly from the app without requiring recovery mode. This simplifies kernel management, making it easier to apply updates or customizations on supported devices.
Installer Improvements
The NetHunter installer has been restructured and now resides in its own Git repository. Key updates include:
Full Magisk Support:The installer now fully supports Magisk, the preferred method for obtaining root access. This includes flashing kernels and support for version 28 and higher.
Command-Line Installation:Users can now install NetHunter using command-line tools like ADB with both Magisk and TWRP methods.
New Features for APatch and KernelSU:Improvements have been made to support advanced configurations using APatch and KernelSU.
Website RevampThe Kali NetHunter subdomain website has undergone significant changes for better usability. The revamped structure provides:
A clear overview of all pre-created images ready for download.
Lists of all supported devices with options for various Android versions and kernels.
Detailed support information for devices like OnePlus 7, showcasing multiple images for different Android versions.
Comprehensive data on supported Android versions and kernels.
This updated website ensures users have easy access to essential resources, streamlining the process of deploying NetHunter.
Kernel and Device Updates
Kali NetHunter’s kernel and device support have been expanded significantly:
Support for 100 Devices: NetHunter now supports over 100 devices, including the addition of Realme X7 Max 5G (RMX3031) and Xiaomi Mi 9 Lite/CC9 (pyxis).
Updated Device Support: Enhancements for popular devices like Nokia 6.1 & 6.1 Plus, Xiaomi Mi 9T, and Xiaomi Pocophone F1 ensure a more stable experience.
Android 15 Support: The first Android 15 device, Xiaomi Mi A3 (xiaomi-laurel), is now supported.
GNOME 47 Desktop Update
Kali Linux 2024.4 introduces the latest GNOME 47 desktop environment, bringing a fresh wave of enhancements and customizability. One of the standout features is the new accent color customization, allowing users to personalize window and shell widgets with their favorite colors. To ensure a seamless and cohesive visual experience, the Kali team has synchronized these settings with the icon theme and legacy GTK window themes, creating multiple theme variants to match each accent color. These improvements are available across all supported desktop environments, offering users a more personalized and visually appealing Kali experience.
How to Upgrade Kali Linux to 2024.4 From Older Release?
If you're looking to get Kali Linux 2024.4, you can download the latest images from the official Kali Linux website. These fresh images contain the latest packages and bug fixes so you can get started right away.
Check out these pages:
If you already have Kali Linux installed on your system, you can simply do a quick update to get the latest packages and bug fixes. This will ensure that you have the latest and greatest version of Kali Linux installed on your system.
Let's see how to upgrade Kali Linux to 2024.4 from any older versions. The Procedure is very simple. It just needs three commands to complete the upgrade.
How to Upgrade Existing Kali Linux to 2024.4?
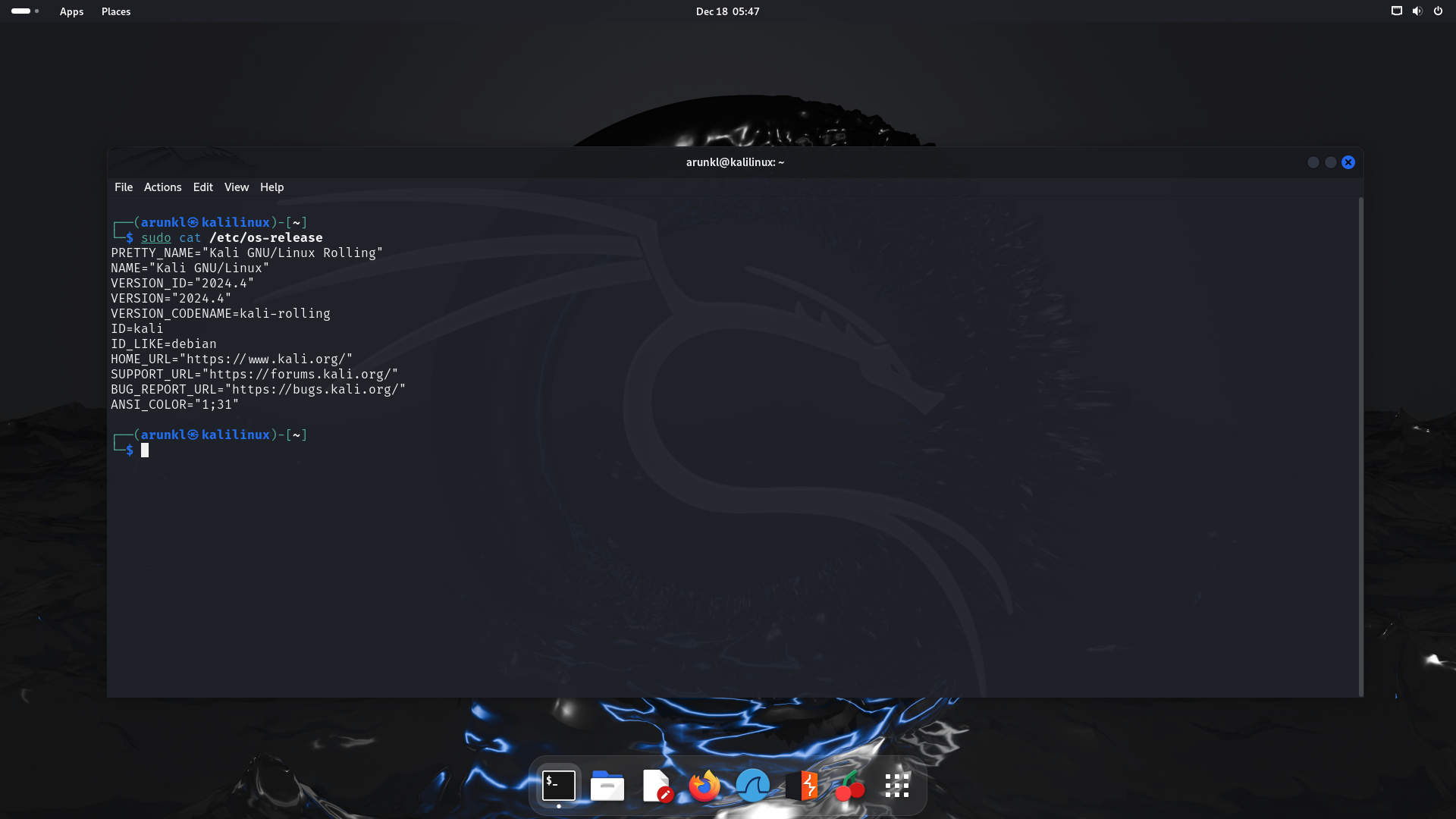
Step 1: Check the current version of Kali Linux
You can check the distribution version using this command:
$ sudo cat /etc/os-releaseStep 2: Update the package lists or the package database
Use this simple command to update the package list:
$ sudo apt updateOR
$ sudo apt-get updateStep 3: Upgrade Kali Linux distribution
You can use the apt upgrade command instead. However, we recommend using dist-upgrade as this command tries resolving dependency issues related to old packages. Note: This process may take up to an hour to complete, depending on your system and internet speed.
$ sudo apt dist-upgradeOR
$ sudo apt-get dist-upgradeStep 4: Check the release version upon the upgrade
Upon successful distribution upgrade, check the distribution version using this command. Since Kali Linux 2024.4 is the latest available version at the time of publishing this post, the system should upgrade to v2024.4.
$ sudo cat /etc/os-releaseIf not, reboot using the below command. The reboot will save all the changes.
$ sudo reboot nowAnd that's it! Your Kali installation should now be up-to-date. This is how you can upgrade Kali Linux to 2024.4.
In conclusion, upgrading Kali Linux to 2024.4 is highly recommended if you want to have the best experience possible when it comes to digital forensics and penetration testing. The transition to Python 3.12, removal of i386 support, and other significant changes make this update particularly important for maintaining a modern and secure testing environment.
Thanks for reading this tutorial post. Visit our website, thesecmaster.com, and our social media page
on Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Telegram, Tumblr, Medium & Instagram, and subscribe to receive updates like this.
You may also like these articles:
What Is New in Kali Linux 2023.4? And, How to Upgrade Kali Linux to 2023.4 From Older Release?
What Is New in Kali Linux 2023.3? And, How to Upgrade Kali Linux to 2023.3?
What Is New in Kali Linux 2023.2? And, How to Upgrade Kali Linux to 2023.2?
What is Kali Linux And What Makes Kali the Hacker's Favourite Distro?
A Step-by-Step Guide to Install Kali Linux on Raspberry Pi 5
Arun KL
Arun KL is a cybersecurity professional with 15+ years of experience in IT infrastructure, cloud security, vulnerability management, Penetration Testing, security operations, and incident response. He is adept at designing and implementing robust security solutions to safeguard systems and data. Arun holds multiple industry certifications including CCNA, CCNA Security, RHCE, CEH, and AWS Security.